Antibodies against trimeric S glycoprotein protect hamsters against SARS-CoV challenge despite their capacity to mediate FcgammaRII-dependent entry into B cells in vitro
- PMID: 17049691
- PMCID: PMC7115629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.08.011
Antibodies against trimeric S glycoprotein protect hamsters against SARS-CoV challenge despite their capacity to mediate FcgammaRII-dependent entry into B cells in vitro
Abstract
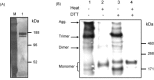
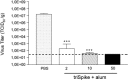
Vaccine-induced antibodies can prevent or, in the case of feline infectious peritonitis virus, aggravate infections by coronaviruses. We investigated whether a recombinant native full-length S-protein trimer (triSpike) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) was able to elicit a neutralizing and protective immune response in animals and analyzed the capacity of anti-S antibodies to mediate antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of virus entry in vitro and enhancement of replication in vivo. SARS-CoV-specific serum and mucosal immunoglobulins were readily detected in immunized animals. Serum IgG blocked binding of the S-protein to the ACE2 receptor and neutralized SARS-CoV infection in vitro. Entry into human B cell lines occurred in a FcgammaRII-dependent and ACE2-independent fashion indicating that ADE of virus entry is a novel cell entry mechanism of SARS-CoV. Vaccinated animals showed no signs of enhanced lung pathology or hepatitis and viral load was undetectable or greatly reduced in lungs following challenge with SARS-CoV. Altogether our results indicate that a recombinant trimeric S protein was able to elicit an efficacious protective immune response in vivo and warrant concern in the safety evaluation of a human vaccine against SARS-CoV.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike antibodies trigger infection of human immune cells via a pH- and cysteine protease-independent FcγR pathway.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(20):10582-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00671-11. Epub 2011 Jul 20. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21775467 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of two severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) vaccine candidates in mice challenged with SARS coronavirus.J Gen Virol. 2006 Mar;87(Pt 3):641-650. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81579-0. J Gen Virol. 2006. PMID: 16476986
-
Antibody-dependent SARS coronavirus infection is mediated by antibodies against spike proteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Aug 22;451(2):208-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.090. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25073113 Free PMC article.
-
SARS vaccine development.Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Jul;11(7):1016-20. doi: 10.3201/1107.050219. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16022774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccine design for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.Viral Immunol. 2005;18(2):327-32. doi: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.327. Viral Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16035944 Review.
Cited by
-
Analytical insights of COVID-19 pandemic.Trends Analyt Chem. 2020 Dec;133:116072. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.116072. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Trends Analyt Chem. 2020. PMID: 33100439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Antibodies in the Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection, and Evaluating Their Contribution to Antibody-Dependent Enhancement of Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 28;23(11):6078. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116078. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological perspectives on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of COVID-19.Mol Biomed. 2021;2(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s43556-020-00015-y. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Mol Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34766001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Host Immune Response.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1313:99-134. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-67452-6_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34661893
-
Recent Insight into SARS-CoV2 Immunopathology and Rationale for Potential Treatment and Preventive Strategies in COVID-19.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 May 14;8(2):224. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020224. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32423059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

