Smc5/6 is required for repair at collapsed replication forks
- PMID: 17030601
- PMCID: PMC1698528
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01335-06
Smc5/6 is required for repair at collapsed replication forks
Abstract
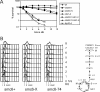
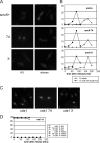
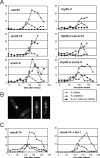
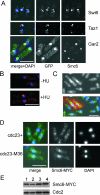
In eukaryotes, three pairs of structural-maintenance-of-chromosome (SMC) proteins are found in conserved multisubunit protein complexes required for chromosomal organization. Cohesin, the Smc1/3 complex, mediates sister chromatid cohesion while two condensin complexes containing Smc2/4 facilitate chromosome condensation. Smc5/6 scaffolds an essential complex required for homologous recombination repair. We have examined the response of smc6 mutants to the inhibition of DNA replication. We define homologous recombination-dependent and -independent functions for Smc6 during replication inhibition and provide evidence for a Rad60-independent function within S phase, in addition to a Rad60-dependent function following S phase. Both genetic and physical data show that when forks collapse (i.e., are not stabilized by the Cds1Chk2 checkpoint), Smc6 is required for the effective repair of resulting lesions but not for the recruitment of recombination proteins. We further demonstrate that when the Rad60-dependent, post-S-phase Smc6 function is compromised, the resulting recombination-dependent DNA intermediates that accumulate following release from replication arrest are not recognized by the G2/M checkpoint.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rhp51-dependent recombination intermediates that do not generate checkpoint signal are accumulated in Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad60 and smc5/6 mutants after release from replication arrest.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):343-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.343-353.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16354704 Free PMC article.
-
Smc5/6 maintains stalled replication forks in a recombination-competent conformation.EMBO J. 2009 Jan 21;28(2):144-55. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.273. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19158664 Free PMC article.
-
Rad62 protein functionally and physically associates with the smc5/smc6 protein complex and is required for chromosome integrity and recombination repair in fission yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(21):9401-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.21.9401-9413.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15485909 Free PMC article.
-
The unnamed complex: what do we know about Smc5-Smc6?Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):251-63. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-9016-8. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308705 Review.
-
The Smc5/6 Complex: New and Old Functions of the Enigmatic Long-Distance Relative.Annu Rev Genet. 2018 Nov 23;52:89-107. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031353. Annu Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 30476445 Review.
Cited by
-
Incision of damaged DNA in the presence of an impaired Smc5/6 complex imperils genome stability.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Dec 1;44(21):10216-10229. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw720. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27536003 Free PMC article.
-
Brc1-dependent recovery from replication stress.J Cell Sci. 2012 Jun 1;125(Pt 11):2753-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103119. Epub 2012 Feb 24. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22366461 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of Ubiquitin and SUMO in DNA Replication and Replication Stress.Front Genet. 2016 May 13;7:87. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00087. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27242895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Smc complexes in DNA damage response.Cell Biosci. 2012 Feb 27;2:5. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-5. Cell Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22369641 Free PMC article.
-
The Smc5/6 complex is required for dissolution of DNA-mediated sister chromatid linkages.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6502-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq546. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20571088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bahler, J., J. Q. Wu, M. S. Longtine, N. G. Shah, A. McKenzie III, A. B. Steever, A. Wach, P. Philippsen, and J. R. Pringle. 1998. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14:943-951. - PubMed
-
- Betts Lindroos, H., L. Strom, T. Itoh, Y. Katou, K. Shirahige, and C. Sjogren. 2006. Chromosomal association of the Smc5/6 complex reveals that it functions in differently regulated pathways. Mol. Cell 22:755-767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
