PHI-1 interacts with the catalytic subunit of myosin light chain phosphatase to produce a Ca(2+) independent increase in MLC(20) phosphorylation and force in avian smooth muscle
- PMID: 17022978
- PMCID: PMC1698950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.09.035
PHI-1 interacts with the catalytic subunit of myosin light chain phosphatase to produce a Ca(2+) independent increase in MLC(20) phosphorylation and force in avian smooth muscle
Abstract
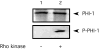
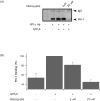
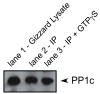
In avian smooth muscles, GTPgammaS produces a Rho kinase mediated increase in PHI-1 phosphorylation and force, but whether this correlation is causal is unknown. We examined the effect of phosphorylated PHI-1 (P-PHI-1) on force and myosin light chain (MLC(20)) phosphorylation at a constant [Ca(2+)]. P-PHI-1, but not PHI-1, increased MLC(20) phosphorylation and force, and phosphorylation of PHI-1 increased the interaction of PHI-1 with PP1c. Microcystin induced a dose-dependent reduction in the binding of PHI-1 to PP1c. These results suggest PHI-1 inhibits myosin light chain phosphatase by interacting with the active site of PP1c to produce a Ca(2+) independent increase in MLC(20) phosphorylation and force.
Figures


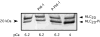
Similar articles
-
PHI-1 induced enhancement of myosin phosphorylation in chicken smooth muscle.FEBS Lett. 2005 Aug 15;579(20):4271-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.06.059. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16081075
-
A role for Rho-kinase in Ca-independent contractions induced by phorbol-12,13-dibutyrate.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009 Mar;36(3):256-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05045.x. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18986333
-
Differential signalling by muscarinic receptors in smooth muscle: m2-mediated inactivation of myosin light chain kinase via Gi3, Cdc42/Rac1 and p21-activated kinase 1 pathway, and m3-mediated MLC20 (20 kDa regulatory light chain of myosin II) phosphorylation via Rho-associated kinase/myosin phosphatase targeting subunit 1 and protein kinase C/CPI-17 pathway.Biochem J. 2003 Aug 15;374(Pt 1):145-55. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021274. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12733988 Free PMC article.
-
[Formation and regulation of myosin light chain kinase and phosphatase complex in smooth muscle: the outlook].Tsitologiia. 1998;40(6):568-78. Tsitologiia. 1998. PMID: 9778739 Review. Russian.
-
Regulation of myosin light-chain phosphorylation and its roles in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology.Hypertens Res. 2022 Jan;45(1):40-52. doi: 10.1038/s41440-021-00733-y. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Hypertens Res. 2022. PMID: 34616031 Review.
Cited by
-
Nonmuscle myosin is regulated during smooth muscle contraction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):H191-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00132.2009. Epub 2009 May 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19429828 Free PMC article.
-
A bioinformatic and computational study of myosin phosphatase subunit diversity.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Aug 1;307(3):R256-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00145.2014. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24898838 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and the Basis for Pharmacologic Treatment of Smooth Muscle Disorders.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Apr;68(2):476-532. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.010652. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27037223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myosin phosphatase isoforms as determinants of smooth muscle contractile function and calcium sensitivity of force production.Microcirculation. 2014 Apr;21(3):239-48. doi: 10.1111/micc.12097. Microcirculation. 2014. PMID: 24112301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging related decreases in NM myosin expression and contractility in a resistance vessel.Front Physiol. 2024 May 14;15:1411420. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1411420. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38808359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gong MC, Cohen P, Kitazawa T, Ikebe M, Masuo M, Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV. Myosin light chain phosphatase activities and the effects of phosphatase inhibitors in tonic and phasic smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:14662–14668. - PubMed
-
- Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: Modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:1325–1358. - PubMed
-
- Hartshorne DJ, Ito M, Erdîdi F. Myosin light chain phosphatase: Subunit composition, interactions and regulation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1998;19:325–341. - PubMed
-
- Ichikawa K, Ito M, Hartshorne DJ. Phosphorylation of the large subunit of myosin phosphatase and inhibition of phosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:4733–4740. - PubMed
-
- Velasco G, Armstrong C, Morrice N, Frame S, Cohen P. Phosphorylation of the regulatory subunit of smooth muscle protein phosphatase 1M at Thr850 induces its dissociation from myosin. FEBS Lett. 2002;527:101–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

