Gene structure and expression of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF56, ORF57, ORF58, and ORF59
- PMID: 17020939
- PMCID: PMC1676266
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01394-06
Gene structure and expression of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF56, ORF57, ORF58, and ORF59
Abstract
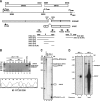
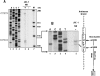
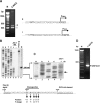
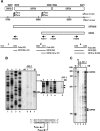
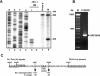
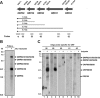
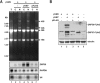
Though similar to those of herpesvirus saimiri and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) genome features more splice genes and encodes many genes with bicistronic or polycistronic transcripts. In the present study, the gene structure and expression of KSHV ORF56 (primase), ORF57 (MTA), ORF58 (EBV BMRF2 homologue), and ORF59 (DNA polymerase processivity factor) were analyzed in butyrate-activated KSHV(+) JSC-1 cells. ORF56 was expressed at low abundance as a bicistronic ORF56/57 transcript that utilized the same intron, with two alternative branch points, as ORF57 for its RNA splicing. ORF56 was transcribed from two transcription start sites, nucleotides (nt) 78994 (minor) and 79075 (major), but selected the same poly(A) signal as ORF57 for RNA polyadenylation. The majority of ORF56 and ORF57 transcripts were cleaved at nt 83628, although other nearby cleavage sites were selectable. On the opposite strand of the viral genome, colinear ORF58 and ORF59 were transcribed from different transcription start sites, nt 95821 (major) or 95824 (minor) for ORF58 and nt 96790 (minor) or 96794 (major) for ORF59, but shared overlapping poly(A) signals at nt 94492 and 94488. Two cleavage sites, at nt 94477 and nt 94469, could be equally selected for ORF59 polyadenylation, but only the cleavage site at nt 94469 could be selected for ORF58 polyadenylation without disrupting the ORF58 stop codon immediately upstream. ORF58 was expressed in low abundance as a monocistronic transcript, with a long 5' untranslated region (UTR) but a short 3' UTR, whereas ORF59 was expressed in high abundance as a bicistronic transcript, with a short 5' UTR and a long 3' UTR similar to those of polycistronic ORF60 and ORF62. Both ORF56 and ORF59 are targets of ORF57 and were up-regulated significantly in the presence of ORF57, a posttranscriptional regulator.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multiple regions of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF59 RNA are required for its expression mediated by viral ORF57 and cellular RBM15.Viruses. 2015 Feb 3;7(2):496-510. doi: 10.3390/v7020496. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25690794 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted disruption of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 in the viral genome is detrimental for the expression of ORF59, K8alpha, and K8.1 and the production of infectious virus.J Virol. 2007 Feb;81(3):1062-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01558-06. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17108026 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 functions as a viral splicing factor and promotes expression of intron-containing viral lytic genes in spliceosome-mediated RNA splicing.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(6):2792-801. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01856-07. Epub 2008 Jan 9. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18184716 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 in viral RNA processing.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(4):1516-28. doi: 10.2741/3322. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV ORF57, a protein of many faces.Viruses. 2015 Feb 10;7(2):604-33. doi: 10.3390/v7020604. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25674768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple regions of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF59 RNA are required for its expression mediated by viral ORF57 and cellular RBM15.Viruses. 2015 Feb 3;7(2):496-510. doi: 10.3390/v7020496. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25690794 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter- and cell-specific transcriptional transactivation by the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57/Mta protein.J Virol. 2007 Dec;81(24):13299-314. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00732-07. Epub 2007 Oct 3. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17913801 Free PMC article.
-
Redefining the genetics of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 via transcriptome-based annotation.Cell Host Microbe. 2010 Jun 25;7(6):516-26. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.05.005. Cell Host Microbe. 2010. PMID: 20542255 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide mapping and screening of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) 3' untranslated regions identify bicistronic and polycistronic viral transcripts as frequent targets of KSHV microRNAs.J Virol. 2014 Jan;88(1):377-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02689-13. Epub 2013 Oct 23. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24155407 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation between viral interferon regulatory factor 4 and RTA to activate a subset of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic promoters.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(2):1021-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00694-11. Epub 2011 Nov 16. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22090118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler, J. E., and J. T. Kadonaga. 2002. The RNA polymerase II core promoter: a key component in the regulation of gene expression. Genes Dev. 16:2583-2592. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Y., M. Ciustea, and R. P. Ricciardi. 2005. Processivity factor of KSHV contains a nuclear localization signal and binding domains for transporting viral DNA polymerase into the nucleus. Virology 340:183-191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

