Phosphorylation of Chk1 by ATR is antagonized by a Chk1-regulated protein phosphatase 2A circuit
- PMID: 17015476
- PMCID: PMC1636880
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00447-06
Phosphorylation of Chk1 by ATR is antagonized by a Chk1-regulated protein phosphatase 2A circuit
Abstract
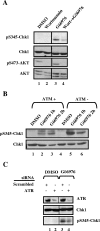
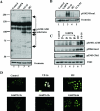
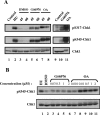
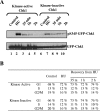
In higher eukaryotic organisms, the checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) contributes essential functions to both cell cycle and checkpoint control. Chk1 executes these functions, in part, by targeting the Cdc25A protein phosphatase for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. In response to genotoxic stress, Chk1 is phosphorylated on serines 317 (S317) and 345 (S345) by the ataxia-telangiectasia-related (ATR) protein kinase. Phosphorylation of Chk1 on these C-terminal serine residues is used as an indicator of Chk1 activation in vivo. Here, we report that inhibition of Chk1 kinase activity paradoxically leads to the accumulation of S317- and S345-phosphorylated Chk1 in vivo and that ATR catalyzes Chk1 phosphorylation under these conditions. We demonstrate that Chk1 phosphorylation by ATR is antagonized by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). Importantly, dephosphorylation of Chk1 by PP2A is regulated, in part, by the kinase activity of Chk1. We propose that the ATR-Chk1-PP2A regulatory circuit functions to keep Chk1 in a low-activity state during an unperturbed cell division cycle but at the same time keeps Chk1 primed to respond rapidly in the event that cells encounter genotoxic stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phosphatase type 2A-dependent and -independent pathways for ATR phosphorylation of Chk1.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7287-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607951200. Epub 2007 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17210576
-
ATR-mediated checkpoint pathways regulate phosphorylation and activation of human Chk1.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jul;21(13):4129-39. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.13.4129-4139.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11390642 Free PMC article.
-
Chk1 C-terminal regulatory phosphorylation mediates checkpoint activation by de-repression of Chk1 catalytic activity.Oncogene. 2009 Jun 18;28(24):2314-23. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.102. Epub 2009 May 4. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19421147 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinases that regulate chromosome stability and their downstream targets.Genome Dyn. 2006;1:131-148. doi: 10.1159/000092505. Genome Dyn. 2006. PMID: 18724058 Review.
-
Cdc25A phosphatase: combinatorial phosphorylation, ubiquitylation and proteolysis.Oncogene. 2004 Mar 15;23(11):2050-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207394. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15021892 Review.
Cited by
-
ALK signaling primes the DNA damage response sensitizing ALK-driven neuroblastoma to therapeutic ATR inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jan 2;121(1):e2315242121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315242121. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38154064 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC6 Regulates Radiosensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Promoting Degradation of Chk1.Cells. 2020 Oct 4;9(10):2237. doi: 10.3390/cells9102237. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33020410 Free PMC article.
-
The fork and the kinase: a DNA replication tale from a CHK1 perspective.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015 Jan-Mar;763:168-80. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 25795119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitization of human cancer cells to gemcitabine by the Chk1 inhibitor MK-8776: cell cycle perturbation and impact of administration schedule in vitro and in vivo.BMC Cancer. 2013 Dec 21;13:604. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-604. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24359526 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC1 and HDAC2 integrate checkpoint kinase phosphorylation and cell fate through the phosphatase-2A subunit PR130.Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 22;9(1):764. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03096-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29472538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakkenist, C. J., and M. B. Kastan. 2003. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421:499-506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
