Sensitization to the conditioned rewarding effects of morphine modulates gene expression in rat hippocampus
- PMID: 17014870
- PMCID: PMC1976342
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.08.012
Sensitization to the conditioned rewarding effects of morphine modulates gene expression in rat hippocampus
Abstract
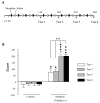
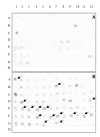
Opiates addiction is characterized by its long-term persistence. In order to study the enduring changes in long-term memory in hippocampus, a pivotal region for this process, we used suppression subtractive hybridization to compare hippocampal gene expression in morphine and saline-treated rats. Animals were subjected to an extended place preference paradigm consisting of four conditioning phases. Sensitization to the reinforcing effects of the drug occurred after three conditioning phases. After 25 days of treatment rats were euthanized and the complementary DNA (cDNA) from the hippocampus of morphine-dependent and saline-treated animals were then screened for differentially expressed cDNAs. The selected 177 clones were then subjected to a microarray procedure and 20 clones were found differentially regulated. The pattern of regulated genes suggests impairments in neurotransmitter release and the activation of neuroprotective pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A morphine-paired environment alters c-Fos expression in the forebrain of rats displaying conditioned place preference or aversion.Behav Neurosci. 2008 Oct;122(5):1078-86. doi: 10.1037/a0012595. Behav Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18823165
-
Repeated morphine treatment alters polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule, glutamate decarboxylase-67 expression and cell proliferation in the adult rat hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jan;21(2):493-500. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03883.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15673448
-
Dorsal hippocampal muscarinic and nicotinic receptors are involved in mediating morphine reward.Behav Brain Res. 2006 Jan 30;166(2):281-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2005.08.010. Epub 2005 Sep 26. Behav Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16191443
-
Role of dorsal hippocampal orexin-1 receptors in associating morphine reward with contextual stimuli.Behav Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;24(4):237-48. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e3283635ee9. Behav Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23787292
-
GABA(A) receptors of hippocampal CA1 regions are involved in the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced place preference.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007 Jan;17(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 16624534
Cited by
-
Role of SIP30 in the development and maintenance of peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain.Pain. 2009 Nov;146(1-2):130-40. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.07.011. Epub 2009 Sep 12. Pain. 2009. PMID: 19748740 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomic mechanisms of opioid action and opioid use disorder: a systematic review of animal models and human studies.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Nov;28(11):4568-4584. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02238-1. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37723284 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine-Induced Dendritic Spine Remodeling in Rat Nucleus Accumbens Is Corticosterone Dependent.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019 Jun 3;22(6):394-401. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz014. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30915438 Free PMC article.
-
Self administration of oxycodone alters synaptic plasticity gene expression in the hippocampus differentially in male adolescent and adult mice.Neuroscience. 2015 Jan 29;285:34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.013. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25446355 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal regulation of peripheral BDNF levels during cocaine and morphine withdrawal: comparison with a natural reward.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Dec 7;18(5):pyu088. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu088. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25522421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ammon S, Mayer P, Riechert U, Tischmeyer H, Hollt V. Microarray analysis of genes expressed in the frontal cortex of rats chronically treated with morphine and after naloxone precipitated withdrawal. Molecular Brain Research. 2003;112:113–125. - PubMed
-
- Andriamampandry C, Muller C, Schmidt-Mutter C, Gobaille S, Spedding M, Aunis D, Maitre M. Mss4 gene is up-regulated in rat brain after chronic treatment with antidepressant and down-regulated when rats are anhedonic. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62:1332–1338. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

