CXCR4 modulates contractility in adult cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 17010372
- PMCID: PMC2002477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.08.008
CXCR4 modulates contractility in adult cardiac myocytes
Abstract
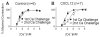
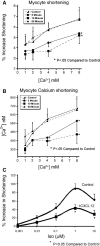
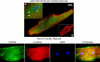
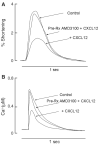
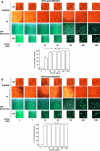
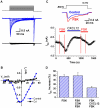
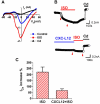
The inflammatory response is critical to the development and progression of heart failure. Chemokines and their receptors are a distinct class of inflammatory modulators that may play a role in mediating myocardial dysfunction in heart failure. Levels of the chemokine CXCL12, also known as stromal cell-derived factor (SDF), and its receptor, CXCR4, are elevated in patients with heart failure, and we undertook this study to determine whether this chemokine system can directly affect cardiac function in the absence of leukocytes. Murine papillary muscles and adult rat cardiac myocytes treated with CXCL12, the only identified ligand of CXCR4, demonstrate blunted inotropic responses to physiologic concentrations of calcium. The negative inotropic effects on cardiac myocytes are accompanied by a proportional diminution of calcium transients. The effects are abrogated by AMD3100, a specific CXCR4 inhibitor. Overexpression of the receptor through adenoviral infection with a CXCR4 construct accentuates the negative inotropic effects of CXCL12 on cardiac myocytes during calcium stimulation. CXCR4 activation also attenuates beta-adrenergic-mediated increases in calcium mobilization and fractional shortening in cardiac myocytes. In electrophysiologic studies, CXCL12 decreases forskolin- and isoproterenol-induced voltage-gated L-type calcium channel activation. These studies demonstrate that activation of CXCR4 results in a direct negative inotropic modulation of cardiac myocyte function. The specific mechanism of action involves alterations of calcium channel activity on the membrane. The presence of functional CXCR4 on cardiac myocytes introduces a new target for treating cardiac dysfunction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CXCR4 gene transfer prevents pressure overload induced heart failure.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Aug;53(2):223-32. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.05.016. Epub 2012 Jun 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22668785 Free PMC article.
-
Adenylyl cyclase-mediated effects contribute to increased Isoprenaline-induced cardiac contractility in TRPM4-deficient mice.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Sep;74:307-17. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.06.007. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24972051
-
β2-Adrenergic receptor signaling in the cardiac myocyte is modulated by interactions with CXCR4.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010 Nov;56(5):548-59. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181f713fe. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20729750 Free PMC article.
-
Structural localization and expression of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in rat heart and isolated cardiac myocytes.J Histochem Cytochem. 2007 Feb;55(2):141-50. doi: 10.1369/jhc.6A7050.2006. Epub 2006 Oct 16. J Histochem Cytochem. 2007. PMID: 17046839
-
Deletion of CXCR4 in cardiomyocytes exacerbates cardiac dysfunction following isoproterenol administration.Gene Ther. 2014 May;21(5):496-506. doi: 10.1038/gt.2014.23. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 24646609 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stroma cell-derived factor-1α signaling enhances calcium transients and beating frequency in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056007. Epub 2013 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23460790 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targets in heart failure gene therapy: current controversies and translational perspectives.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Apr;1254:42-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06520.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22548568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of RNA-Seq and Machine Learning Identifies Hub Genes for Empagliflozin Benefitable Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Oct 18;16:4733-4749. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S429096. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37872956 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in ventricular remodelling and clinical status during the year following a single administration of stromal cell-derived factor-1 non-viral gene therapy in chronic ischaemic heart failure patients: the STOP-HF randomized Phase II trial.Eur Heart J. 2015 Sep 1;36(33):2228-38. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv254. Epub 2015 Jun 7. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 26056125 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ablation of CXCR4 expression in cardiomyocytes exacerbates isoproterenol‑induced cell death and heart failure.Int J Mol Med. 2023 Feb;51(2):13. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5216. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36579657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aukrust P, Ueland T, Muller F, Andreassen AK, Nordoy I, Aas H, et al. Elevated circulating levels of C-C chemokines in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1998;97(12):1136–43. - PubMed
-
- Zou Y-R, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, Taniuchi I, Littman DR. Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature. 1998;393(6685):595. - PubMed
-
- Tachibana K, Hirota S, Iizasa H, Yoshida H, Kawabata K, Kataoka Y, et al. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature. 1998;393(6685):591–4. - PubMed
-
- Oh SB, Endoh T, Simen AA, Ren D, Miller RJ. Regulation of calcium currents by chemokines and their receptors. J Neuroimmunol. 2002;123(1–2):66–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

