Commonly dysregulated genes in murine APL cells
- PMID: 17008535
- PMCID: PMC1785140
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-036640
Commonly dysregulated genes in murine APL cells
Abstract
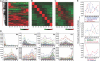
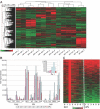
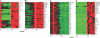
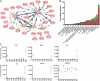
To identify genes that are commonly dysregulated in a murine model of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), we first defined gene expression patterns during normal murine myeloid development; serial gene expression profiling studies were performed with primary murine hematopoietic progenitors that were induced to undergo myeloid maturation in vitro with G-CSF. Many genes were reproducibly expressed in restricted developmental "windows," suggesting a structured hierarchy of expression that is relevant for the induction of developmental fates and/or differentiated cell functions. We compared the normal myeloid developmental transcriptome with that of APL cells derived from mice expressing PML-RARalpha under control of the murine cathepsin G locus. While many promyelocyte-specific genes were highly expressed in all APL samples, 116 genes were reproducibly dysregulated in many independent APL samples, including Fos, Jun, Egr1, Tnf, and Vcam1. However, this set of commonly dysregulated genes was expressed normally in preleukemic, early myeloid cells from the same mouse model, suggesting that dysregulation occurs as a "downstream" event during disease progression. These studies suggest that the genetic events that lead to APL progression may converge on common pathways that are important for leukemia pathogenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PML-RARalpha initiates leukemia by conferring properties of self-renewal to committed promyelocytic progenitors.Leukemia. 2009 Aug;23(8):1462-71. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.63. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Leukemia. 2009. PMID: 19322209 Free PMC article.
-
High-penetrance mouse model of acute promyelocytic leukemia with very low levels of PML-RARalpha expression.Blood. 2003 Sep 1;102(5):1857-65. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3779. Epub 2003 May 15. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12750176
-
PML/RARalpha and FLT3-ITD induce an APL-like disease in a mouse model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jun 11;99(12):8283-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.122233699. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12060771 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the molecular pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2014 Mar;27(1):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2014.04.006. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24907012 Review.
-
In vivo analysis of the molecular pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia in the mouse and its therapeutic implications.Oncogene. 1999 Sep 20;18(38):5278-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203088. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10498880 Review.
Cited by
-
PML-RARA can increase hematopoietic self-renewal without causing a myeloproliferative disease in mice.J Clin Invest. 2011 Apr;121(4):1636-45. doi: 10.1172/JCI42953. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21364283 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic mutations and germline sequence variants in the expressed tyrosine kinase genes of patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2008 May 1;111(9):4797-808. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-113027. Epub 2008 Feb 12. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18270328 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling in acute promyelocytic leukemia.Leukemia. 2013 Jul;27(7):1548-1557. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.68. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Leukemia. 2013. PMID: 23455394 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of PML-RARA in the hematopoietic progenitor cells of Ctsg-PML-RARA mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046529. Epub 2012 Oct 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056333 Free PMC article.
-
Chemosensitization of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) following mobilization by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100.Blood. 2009 Jun 11;113(24):6206-14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-162123. Epub 2008 Dec 2. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19050309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Debernardi S, Lillington DM, Chaplin T, et al. Genome-wide analysis of acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype reveals a unique pattern of homeobox gene expression distinct from those with translocation-mediated fusion events. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2003;37:149–158. - PubMed
-
- Kohlmann A, Schoch C, Schnittger S, et al. Molecular characterization of acute leukemias by use of microarray technology. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2003;37:396–405. - PubMed
-
- Bullinger L, Döhner K, Bair E, et al. Use of gene-expression profiling to identify prognostic subclasses in adult acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1605–1616. - PubMed
-
- Staber PB, Linkesch W, Zauner D, et al. Common alterations in gene expression and increased proliferation in recurrent acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene. 2004;23:894–904. - PubMed
-
- Valk PJM, Verhaak RGW, Beijen MA, et al. Prognostically useful gene-expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1617–1628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

