Exomer: A coat complex for transport of select membrane proteins from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane in yeast
- PMID: 17000877
- PMCID: PMC2064389
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200605106
Exomer: A coat complex for transport of select membrane proteins from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane in yeast
Abstract
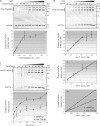
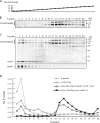
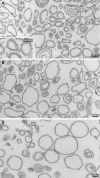
A yeast plasma membrane protein, Chs3p, transits to the mother-bud neck from a reservoir comprising the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and endosomal system. Two TGN/endosomal peripheral proteins, Chs5p and Chs6p, and three Chs6p paralogues form a complex that is required for the TGN to cell surface transport of Chs3p. The role of these peripheral proteins has not been clear, and we now provide evidence that they create a coat complex required for the capture of membrane proteins en route to the cell surface. Sec7p, a Golgi protein required for general membrane traffic and functioning as a nucleotide exchange factor for the guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein Arf1p, is required to recruit Chs5p to the TGN surface in vivo. Recombinant forms of Chs5p, Chs6p, and the Chs6p paralogues expressed in baculovirus form a complex of approximately 1 MD that binds synthetic liposomes in a reaction requiring acidic phospholipids, Arf1p, and the nonhydrolyzable GTPgammaS. The complex remains bound to liposomes centrifuged on a sucrose density gradient. Thin section electron microscopy reveals a spiky coat structure on liposomes incubated with the full complex, Arf1p, and GTPgammaS. We termed the novel coat exomer for its role in exocytosis from the TGN to the cell surface. Unlike other coats (e.g., coat protein complex I, II, and clathrin/adaptor protein complex), the exomer does not form buds or vesicles on liposomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chs5/6 complex: a multiprotein complex that interacts with and conveys chitin synthase III from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Oct;17(10):4157-66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-03-0210. Epub 2006 Jul 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16855022 Free PMC article.
-
Arf1p, Chs5p and the ChAPs are required for export of specialized cargo from the Golgi.EMBO J. 2006 Mar 8;25(5):943-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601007. Epub 2006 Feb 23. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16498409 Free PMC article.
-
Exomer complex regulates protein traffic at the TGN through differential interactions with cargos and clathrin adaptor complexes.FASEB J. 2021 Jun;35(6):e21615. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002610R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33978245 Free PMC article.
-
Domains of the TGN: coats, tethers and G proteins.Traffic. 2004 May;5(5):315-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9219.2004.00182.x. Traffic. 2004. PMID: 15086781 Review.
-
Mechanism of formation of post Golgi vesicles from TGN membranes: Arf-dependent coat assembly and PKC-regulated vesicle scission.Biocell. 1996 Dec;20(3):287-300. Biocell. 1996. PMID: 9031596 Review.
Cited by
-
Sorting signals that mediate traffic of chitin synthase III between the TGN/endosomes and to the plasma membrane in yeast.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46386. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046386. Epub 2012 Oct 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056294 Free PMC article.
-
Direct trafficking pathways from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov;107:112-125. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.04.001. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32317144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Sec14 domain protein is required for photoautotrophic growth and chloroplast vesicle formation in Arabidopsis thaliana.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 21;117(16):9101-9111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916946117. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32245810 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane traffic within the Golgi apparatus.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:113-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.24.110707.175421. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19575639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Golgi export of the Kir2.1 channel is driven by a trafficking signal located within its tertiary structure.Cell. 2011 Jun 24;145(7):1102-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.007. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21703452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonny, B., S. Beraud-Fufour, P. Chardin, and M. Chabre. 1997. N-terminal hydrophobic residues of the G-protein ADP-ribosylation factor-1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry. 36:4675–4684. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe, C., L. Orci, T. Yeung, M. Hosobuchi, S. Hamamoto, N. Salama, M.F. Rexach, M. Ravazzola, M. Amherdt, and R. Schekman. 1994. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 77:895–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

