Controlled release of chlorhexidine from UDMA-TEGDMA resin
- PMID: 16998139
- PMCID: PMC2242729
- DOI: 10.1177/154405910608501016
Controlled release of chlorhexidine from UDMA-TEGDMA resin
Abstract
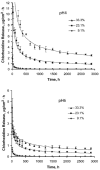
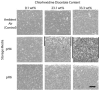
Chlorhexidine salts are available in various formulations for dental applications. This study tested the hypothesis that the release of chlorhexidine from a urethane dimethacrylate and triethylene glycol dimethacrylate resin system can be effectively controlled by the chlorhexidine diacetate content and pH. The filler concentrations were 9.1, 23.1, or 33.3 wt%, and the filled resins were exposed to pH 4 and pH 6 acetate buffers. The results showed that Fickian diffusion was the dominant release mechanism. The rates of release were significantly higher in pH 4 buffer, which was attributed to the increase of chlorhexidine diacetate solubility at lower pH. The higher level of filler loading reduced the degree of polymerization, leading to a greater loss of organic components and higher chlorhexidine release rates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of filler content on the profile of released biodegradation products in micro-filled bis-GMA/TEGDMA dental composite resins.Biomaterials. 1999 Oct;20(20):1897-908. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(99)00087-3. Biomaterials. 1999. PMID: 10514066
-
Effect of CaF2 content on rate of fluoride release from filled resins.J Dent Res. 2005 May;84(5):440-4. doi: 10.1177/154405910508400508. J Dent Res. 2005. PMID: 15840780
-
Influence of silanated filler content on the biodegradation of bisGMA/TEGDMA dental composite resins.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007 Apr;81(1):75-84. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.31004. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007. PMID: 17109416
-
Genetic and cellular toxicology of dental resin monomers.J Dent Res. 2006 Oct;85(10):870-7. doi: 10.1177/154405910608501001. J Dent Res. 2006. PMID: 16998124 Review.
-
How much do resin-based dental materials release? A meta-analytical approach.Dent Mater. 2011 Aug;27(8):723-47. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2011.05.001. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Dent Mater. 2011. PMID: 21664675 Review.
Cited by
-
Limitations in bonding to dentin and experimental strategies to prevent bond degradation.J Dent Res. 2011 Aug;90(8):953-68. doi: 10.1177/0022034510391799. Epub 2011 Jan 10. J Dent Res. 2011. PMID: 21220360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The study of release of chlorhexidine from preparations with modified thermosensitive poly-N-isopropylacrylamide microspheres.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:243707. doi: 10.1100/2012/243707. Epub 2012 Apr 26. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22629123 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial dental adhesive resins containing nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018 Dec 1;93:931-943. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.08.060. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018. PMID: 30274130 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical properties and sustainable bacterial resistance effect of strontium-modified phosphate-based glass microfiller in dental composite resins.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 18;13(1):17763. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44490-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37853055 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of water-aging on the antimicrobial activities of an ORMOSIL-containing orthodontic acrylic resin.Acta Biomater. 2013 Jun;9(6):6964-73. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.02.031. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23485857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addy M, Rawle L, Handley R, Newman HN, Coventry JF. The development and in vitro evaluation of acrylic strips and dialysis tubing for local drug delivery. J Periodontol. 1982;53:693–699. - PubMed
-
- Anusavice KJ, Zhang NZ, Shen C. Effect of CaF2 content on rate of fluoride release from filled resins. J Dent Res. 2005;84:440–444. - PubMed
-
- Axelsson P, Lindhe J. Efficacy of mouthrinses in inhibiting dental plaque and gingivitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1987;14:205–212. - PubMed
-
- Coury A. Chemical and biochemical degradation of polymers. In: Ratner BD, Hoffman AS, Schoen FJ, Lemons JE, editors. Biomaterials science. 2nd. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press; 2004. pp. 411–430.
-
- Coventry J, Newman HN. Experimental use of a slow release device employing chlorhexidine gluconate in areas of acute periodontal inflammation. J Clin Periodontol. 1982;9:129–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

