Aberrant Forkhead box O1 function is associated with impaired hepatic metabolism
- PMID: 16997836
- PMCID: PMC2665253
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2006-0541
Aberrant Forkhead box O1 function is associated with impaired hepatic metabolism
Abstract
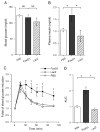
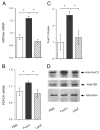
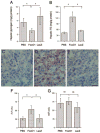
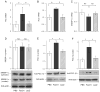
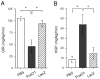
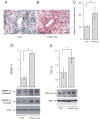
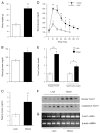
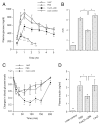
FoxO1 plays an important role in mediating the effect of insulin on hepatic metabolism. Increased FoxO1 activity is associated with reduced ability of insulin to regulate hepatic glucose production. However, the underlying mechanism and physiology remain unknown. We studied the effect of FoxO1 on the ability of insulin to regulate hepatic metabolism in normal vs. insulin-resistant liver under fed and fasting conditions. FoxO1 gain of function, as a result of adenovirus-mediated or transgenic expression, augmented hepatic gluconeogenesis, accompanied by decreased glycogen content and increased fat deposition in liver. Mice with excessive FoxO1 activity exhibited impaired glucose tolerance. Conversely, FoxO1 loss of function, caused by hepatic production of its dominant-negative variant, suppressed hepatic gluconeogenesis, resulting in enhanced glucose disposal and improved insulin sensitivity in db/db mice. FoxO1 expression becomes deregulated, culminating in increased nuclear localization and accounting for its increased transcription activity in livers of both high fat-induced obese mice and diabetic db/db mice. Increased FoxO1 activity resulted in up-regulation of hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1beta, fatty acid synthase, and acetyl CoA carboxylase expression, accounting for increased hepatic fat infiltration. These data indicate that hepatic FoxO1 deregulation impairs the ability of insulin to regulate hepatic metabolism, contributing to the development of hepatic steatosis and abnormal metabolism in diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Foxo1 function is associated with improved fasting glycemia in diabetic mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Oct;285(4):E718-28. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00156.2003. Epub 2003 Jun 3. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12783775
-
Pancreatic-derived factor promotes lipogenesis in the mouse liver: role of the Forkhead box 1 signaling pathway.Hepatology. 2011 Jun;53(6):1906-16. doi: 10.1002/hep.24295. Epub 2011 May 2. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21412813
-
MicroRNA-21 regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by targeting FOXO1.Gene. 2017 Sep 5;627:194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.024. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28627440
-
FoxO1 integrates insulin signaling to VLDL production.Cell Cycle. 2008 Oct;7(20):3162-70. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.20.6882. Epub 2008 Oct 27. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18927507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting FoxO1 for hypertriglyceridemia.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Aug;12(9):1245-55. doi: 10.2174/138945011796150262. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21443465 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect and the probable mechanisms of silibinin in regulating insulin resistance in the liver of rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013 Mar;46(3):270-7. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20122551. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013. PMID: 23532271 Free PMC article.
-
FoxO1 links insulin resistance to proinflammatory cytokine IL-1beta production in macrophages.Diabetes. 2009 Nov;58(11):2624-33. doi: 10.2337/db09-0232. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19651810 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of hepatic FoxO1/3/4 genes in mice significantly impacts on glucose metabolism through downregulation of gluconeogenesis and upregulation of glycolysis.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 28;8(8):e74340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074340. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24015318 Free PMC article.
-
FoxO6 in glucose metabolism (FoxO6).J Diabetes. 2013 Sep;5(3):233-40. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12027. Epub 2013 May 28. J Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23324123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Forkhead Box O6 (FoxO6) Depletion Attenuates Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Protects against Fat-induced Glucose Disorder in Mice.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 19;290(25):15581-15594. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.650994. Epub 2015 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25944898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pilkis SJ, Granner DK. Molecular physiology of the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:885–909. - PubMed
-
- Giaccari A, Morviducci L, Pastore L, Zorretta D, Sbraccia P, Maroccia E, Buongiorno A, Tamburrano G. Relative contribution of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis to hepatic glucose production in control and diabetic rats. A re-examination in the presence of euglyceamia. Diabetologia. 1998;41:307–314. - PubMed
-
- Boden G, Chen X, Stein TP. Gluconeogenesis in moderately and severely hyperglycemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;280:E23–E30. - PubMed
-
- Kaestner KH, Knochel W, Martinez DE. Unified nomenclature for the winged helix/forkhead transcription factors. Gene Dev. 2000;14:142–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

