Fatty acids from Plasmodium falciparum down-regulate the toxic activity of malaria glycosylphosphatidylinositols
- PMID: 16988223
- PMCID: PMC1594897
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01934-05
Fatty acids from Plasmodium falciparum down-regulate the toxic activity of malaria glycosylphosphatidylinositols
Abstract
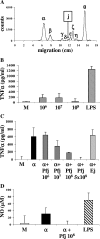
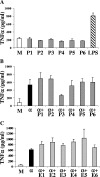
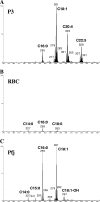
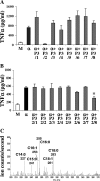
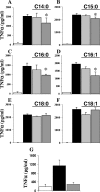
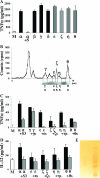
Plasmodium falciparum malaria kills roughly 2.5 million people, mainly children, annually. Much of this mortality is thought to arise from the actions of a malarial toxin. This toxin, identified as glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI), is a major pathogenicity determinant in malaria. A malarial molecule, Pfj, labeled by [3H]glucosamine like the GPIs, was identified as a non-GPI molecule. Here we show that Pfj is able to down-regulate tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) production induced by the GPI of P. falciparum. Mass spectrometry analysis showed that Pfj was not a single molecule but represented a number of molecules. Separation methods, such as cation-exchange chromatography and thin-layer chromatography, were used to isolate and identify the following four main fatty acids responsible for the inhibitory effect on TNF-alpha production: myristic, pentadecanoic, palmitic, and palmitoleic acids. This regulatory effect on cytokine production suggests that there is balanced bioactivity for the different categories of malarial lipids.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-induced cardiac myocyte death might contribute to the fatal outcome of Plasmodium falciparum malaria.Apoptosis. 2008 Jul;13(7):857-66. doi: 10.1007/s10495-008-0217-6. Apoptosis. 2008. PMID: 18470700
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors of Plasmodium falciparum: molecular characterization and naturally elicited antibody response that may provide immunity to malaria pathogenesis.J Exp Med. 2000 Dec 4;192(11):1563-76. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.11.1563. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 11104799 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acids isolated from Toxoplasma gondii reduce glycosylphosphatidylinositol-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha production through inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway.Infect Immun. 2007 Jun;75(6):2886-93. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01431-06. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17387164 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to glycosylphosphatidylinositol, the dominant TNF-alpha-inducing toxin of Plasmodium falciparum: prospects for the immunotherapy of severe malaria.Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1993 Dec;87(6):617-26. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1993.11812820. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1993. PMID: 8122925 Review.
-
Plasmodium falciparum GPI toxin: a common foe for man and mosquito.Acta Trop. 2010 Jun;114(3):162-5. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Acta Trop. 2010. PMID: 19539593 Review.
Cited by
-
A Metabolomic Investigation of the Effect of Eosin B on Game-tocyte of Plasmodium falciparum Using 1HNMR Spectroscopy.Iran J Parasitol. 2019 Oct-Dec;14(4):592-603. Iran J Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 32099562 Free PMC article.
-
Newly described pattern recognition receptors team up against intracellular pathogens.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Aug;13(8):551-65. doi: 10.1038/nri3479. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23846113 Review.
-
Lipid Biomarkers in Acute Myocardial Infarction Before and After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention by Lipidomics Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jun 18;24:4175-4182. doi: 10.12659/MSM.908732. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29913478 Free PMC article.
-
Blood coagulation, inflammation, and malaria.Microcirculation. 2008 Feb;15(2):81-107. doi: 10.1080/10739680701451516. Microcirculation. 2008. PMID: 18260002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic-Induced Disruption of Gut Microbiota Alters Local Metabolomes and Immune Responses.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 24;9:99. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00099. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31069173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azzouz, N., H. Shams-Eldin, and R. T. Schwarz. 2005. Removal of phospholipid contaminants through precipitation of glycosylphosphatidylinositols. Anal. Biochem. 343:152-158. - PubMed
-
- Bodennec, J., O. Koul, I. Aguado, G. Brichon, G. Zwingelstein, and J. Portoukalian. 2000. A procedure for fractionation of sphingolipid classes by solid-phase extraction on aminopropyl cartridges. J. Lipid Res. 41:1524-1531. - PubMed
-
- Debierre-Grockiego, F., N. Azzouz, J. Schmidt, J. F. Dubremetz, H. Geyer, R. Geyer, R. Weingart, R. R. Schmidt, and R. T. Schwarz. 2003. Roles of glycosylphosphatidylinositols of Toxoplasma gondii. Induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 278:32987-32993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

