Molecular cross-talk between the NFkappaB and STAT3 signaling pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 16984731
- PMCID: PMC1584297
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.06274
Molecular cross-talk between the NFkappaB and STAT3 signaling pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
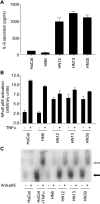
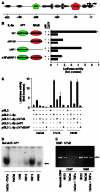
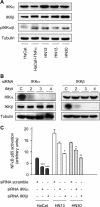
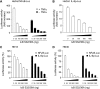
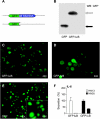
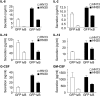
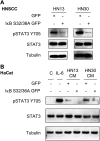
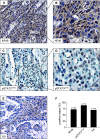
The development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) involves the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations in tumor-suppressor proteins, together with the persistent activation of growth-promoting signaling pathways. The activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a frequent event in HNSCC. However, EGFR-independent mechanisms also contribute to the activation of key intracellular signaling routes, including signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3), nuclear factor kappaB (NFkappaB), and Akt. Indeed, the autocrine activation of the gp130 cytokine receptor in HNSCC cells by tumor-released cytokines, such as IL-6, can result in the EGFR-independent activation of STAT3. In this study, we explored the nature of the molecular mechanism underlying enhanced IL-6 secretion in HNSCC cells. We found that HNSCC cells display an increased activity of the IL-6 promoter, which is dependent on the presence of an intact NFkappaB site. Furthermore, NFkappaB inhibition downregulated IL-6 gene and protein expression, and decreased the release of multiple cytokines. Interestingly, interfering with NFkappaB function also prevented the autocrine/paracrine activation of STAT3 in HNSCC cells. These findings demonstrate a cross-talk between the NFkappaB and the STAT3 signaling systems, and support the emerging notion that HNSCC results from the aberrant activity of a signaling network.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence that TNF-TNFR1-TRADD-TRAF2-RIP-TAK1-IKK pathway mediates constitutive NF-kappaB activation and proliferation in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncogene. 2007 Mar 1;26(10):1385-97. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209945. Epub 2006 Sep 4. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16953224
-
Guggulsterone (GS) inhibits smokeless tobacco and nicotine-induced NF-κB and STAT3 pathways in head and neck cancer cells.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Mar;32(3):368-80. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq278. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21177768
-
Cross-talk between G protein-coupled receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathways contributes to growth and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 15;66(24):11831-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2876. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17178880
-
Role of activated nuclear factor-kappaB in the pathogenesis and therapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Head Neck. 2007 Oct;29(10):959-71. doi: 10.1002/hed.20615. Head Neck. 2007. PMID: 17405170 Review.
-
STAT signaling in head and neck cancer.Oncogene. 2000 May 15;19(21):2489-95. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203483. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10851047 Review.
Cited by
-
PI3K-PTEN dysregulation leads to mTOR-driven upregulation of the core clock gene BMAL1 in normal and malignant epithelial cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):42393-42407. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9877. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27285754 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin reduced deep vein thrombosis in ApoE gene deleted mice with hyperlipidemia through non-lipid lowering effects.Thromb Res. 2013 Mar;131(3):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 29. Thromb Res. 2013. PMID: 23276528 Free PMC article.
-
Survival response of hippocampal neurons under low oxygen conditions induced by Hippophae rhamnoides is associated with JAK/STAT signaling.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 6;9(2):e87694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087694. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24516559 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB and stat3 transcription factor signatures differentiate HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2015 Oct 15;137(8):1879-89. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29558. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25857630 Free PMC article.
-
Logic-Based and Cellular Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Bortezomib Responses in U266 Human Myeloma Cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Sep;354(3):448-58. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.224766. Epub 2015 Jul 10. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 26163548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Hunter KD, Parkinson EK, Harrison PR. Profiling early head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:127–135. - PubMed
-
- Forastiere A, Koch W, Trotti A, Sidransky D. Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1890–1900. - PubMed
-
- Dassonville O, Formento JL, Francoual M, Ramaioli A, Santini J, Schneider M, Demard F, Milano G. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and survival in upper aerodigestive tract cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11:1873–1878. - PubMed
-
- Grandis JR, Tweardy DJ. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3579–3584. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
