Analysis of RNase P protein (rnpA) expression in Bacillus subtilis utilizing strains with suppressible rnpA expression
- PMID: 16980484
- PMCID: PMC1595511
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00756-06
Analysis of RNase P protein (rnpA) expression in Bacillus subtilis utilizing strains with suppressible rnpA expression
Abstract
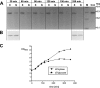
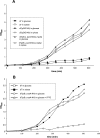
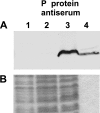
Bacterial RNase P is composed of an RNA subunit and a single protein subunit (encoded by the rnpB and rnpA genes, respectively). We constructed Bacillus subtilis mutant strains that conditionally express the RNase P protein under control of the xylose promoter (P(xyl)). In one strain (d7), rnpA expression was efficiently repressed in the absence of the inducer xylose, leading to cell growth arrest. Growth could be restored by a second functional rnpA allele. This is the first RNase P protein knockdown strain, providing the first direct proof that the rnpA gene is essential in B. subtilis and, by inference, in other bacteria. We further show (i) that, in the wild-type context, rnpA expression is attenuated by transcriptional polarity and (ii) that translation of rnpA mRNA in B. subtilis can be initiated at two alternative start codons. His-tagged RNase P protein variants are functional in vivo and permit purification of in vivo-assembled holoenzymes by affinity chromatography. Simultaneous expression of plasmid-encoded RNase P RNA and His-tagged protein increased RNase P holoenzyme yields. Massive overproduction of RNase P protein in strain d7 is compatible with cell viability.
Figures
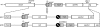


Similar articles
-
Function of heterologous and truncated RNase P proteins in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Nov;66(3):801-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05962.x. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17919279
-
On the role of the appended P19 element in type A RNAs of bacterial RNase P.Biochemistry. 2014 Mar 25;53(11):1810-7. doi: 10.1021/bi4011013. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24580115
-
Physical mapping and nucleotide sequence of the rnpA gene that encodes the protein component of ribonuclease P in Escherichia coli.Gene. 1985;38(1-3):85-93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90206-9. Gene. 1985. PMID: 2415431
-
Potential contact sites between the protein and RNA subunit in the Bacillus subtilis RNase P holoenzyme.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jan 25;315(4):551-60. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5261. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11812129
-
Essential genes in Bacillus subtilis: a re-evaluation after ten years.Mol Biosyst. 2013 Jun;9(6):1068-75. doi: 10.1039/c3mb25595f. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Mol Biosyst. 2013. PMID: 23420519 Review.
Cited by
-
Minor changes largely restore catalytic activity of archaeal RNase P RNA from Methanothermobacter thermoautotrophicus.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(1):231-42. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn915. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19036794 Free PMC article.
-
RNase P Inhibitors Identified as Aggregators.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Jul 16;65(8):e0030021. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00300-21. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33972249 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence Analysis and Comparative Study of the Protein Subunits of Archaeal RNase P.Biomolecules. 2016 Apr 20;6(2):22. doi: 10.3390/biom6020022. Biomolecules. 2016. PMID: 27104580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of RNA-based and protein-only RNases P from bacteria encoding both enzyme types.RNA. 2023 Mar;29(3):376-391. doi: 10.1261/rna.079459.122. Epub 2023 Jan 5. RNA. 2023. PMID: 36604113 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and in vitro investigation of bacterial type B RNase P interaction with tRNA 3'-CCA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(6):2060-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm005. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17355991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong, H., L. A. Kirsebom, and L. Nilsson. 1996. Growth rate regulation of 4.5 S RNA and M1 RNA the catalytic subunit of Escherichia coli RNase P. J. Mol. Biol. 261:303-308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

