Proteasome inhibition reveals that a functional preintegration complex intermediate can be generated during restriction by diverse TRIM5 proteins
- PMID: 16973579
- PMCID: PMC1617233
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01052-06
Proteasome inhibition reveals that a functional preintegration complex intermediate can be generated during restriction by diverse TRIM5 proteins
Abstract
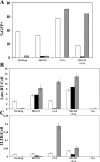
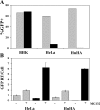
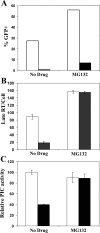
The primate TRIM5 proteins constitute a class of restriction factors that prevent host cell infection by retroviruses from different species. The TRIM5 proteins act early after virion entry and prevent viral reverse transcription products from accumulating. We recently found that proteasome inhibitors altered the rhesus monkey TRIM5alpha restriction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), allowing reverse transcription products to accumulate even though viral infection remained blocked. To assess whether sensitivity to proteasome inhibitors was a common feature of primate TRIM5 proteins, we conducted a similar analysis of restriction mediated by owl monkey TRIM-cyclophilin A (CypA) or human TRIM5alpha. Similar to rhesus monkey TRIM5alpha restriction, proteasome inhibition prevented owl monkey TRIM-CypA restriction of HIV-1 reverse transcription, even though HIV-1 infection and the output of 2-LTR circles remained impaired. Likewise, proteasome inhibition alleviated human TRIM5alpha restriction of N-tropic murine leukemia virus reverse transcription. Finally, HIV-1 reverse transcription products escaping rhesus TRIM5alpha restriction by proteasome inhibition were fully competent for integration in vitro, demonstrating that TRIM5alpha likely prevents the viral cDNA from accessing chromosomal target DNA. Collectively, these data indicate that the diverse TRIM5 proteins inhibit retroviral infection in multiple ways and that inhibition of reverse transcription products is not necessary for TRIM5-mediated restriction of retroviral infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cyclophilin A and TRIM5alpha independently regulate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity in human cells.J Virol. 2006 Mar;80(6):2855-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.6.2855-2862.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16501094 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophilin A facilitates HIV-1 integration.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0094724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00947-24. Epub 2024 Oct 31. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39480090
-
Vif counteracts a cyclophilin A-imposed inhibition of simian immunodeficiency viruses in human cells.J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(15):8080-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02727-06. Epub 2007 May 23. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17522232 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Pharmacological treatments in panic disorder in adults: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 28;11(11):CD012729. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012729.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38014714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterisation of assembly and ubiquitylation by the RBCC motif of Trim5α.Sci Rep. 2016 May 27;6:26837. doi: 10.1038/srep26837. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27230667 Free PMC article.
-
RING Dimerization Links Higher-Order Assembly of TRIM5α to Synthesis of K63-Linked Polyubiquitin.Cell Rep. 2015 Aug 4;12(5):788-97. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.072. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26212332 Free PMC article.
-
The retroviral restriction factor TRIM5alpha.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2007 Mar;9(2):167-73. doi: 10.1007/s11908-007-0013-4. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2007. PMID: 17324355
-
Tripartite motif proteins: an emerging antiviral protein family.Future Virol. 2019 Feb;14(2):107-122. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2018-0161. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Future Virol. 2019. PMID: 31406497 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Functional evidence for the involvement of microtubules and dynein motor complexes in TRIM5α-mediated restriction of retroviruses.J Virol. 2014 May;88(10):5661-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03717-13. Epub 2014 Mar 5. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24600008 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

