TWEAK/Fn14 interaction regulates RANTES production, BMP-2-induced differentiation, and RANKL expression in mouse osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells
- PMID: 16945157
- PMCID: PMC1779446
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2038
TWEAK/Fn14 interaction regulates RANTES production, BMP-2-induced differentiation, and RANKL expression in mouse osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells
Abstract
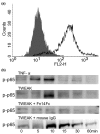
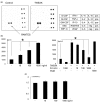
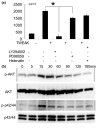
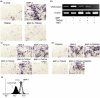
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK), a member of the TNF family, is a multifunctional cytokine that regulates cell growth, migration, and survival principally through a TWEAK receptor, fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14). However, its physiological roles in bone are largely unknown. We herein report various effects of TWEAK on mouse osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. MC3T3-E1 cells expressed Fn14 and produced RANTES (regulated upon activation, healthy T cell expressed and secreted) upon TWEAK stimulation through PI3K-Akt, but not nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), pathway. In addition, TWEAK inhibited bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2-induced expression of osteoblast differentiation markers such as alkaline phosphatase through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) Erk pathway. Furthermore, TWEAK upregulated RANKL (receptor activation of NF-kappaB ligand) expression through MAPK Erk pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. All these effects of TWEAK on MC3T3-E1 cells were abolished by mouse Fn14-Fc chimera. We also found significant TWEAK mRNA or protein expression in osteoblast- and osteoclast-lineage cell lines or the mouse bone tissue, respectively. Finally, we showed that human osteoblasts expressed Fn14 and induced RANTES and RANKL upon TWEAK stimulation. Collectively, TWEAK/Fn14 interaction regulates RANTES production, BMP-2-induced differentiation, and RANKL expression in MC3T3-E1 cells. TWEAK may thus be a novel cytokine that regulates several aspects of osteoblast function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and TNFalpha induce the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent expression of sclerostin in human osteoblasts.J Bone Miner Res. 2009 Aug;24(8):1434-49. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.090305. J Bone Miner Res. 2009. PMID: 19292615
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins, extracellular matrix, and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways are required for osteoblast-specific gene expression and differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells.J Bone Miner Res. 2002 Jan;17(1):101-10. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.1.101. J Bone Miner Res. 2002. PMID: 11771655
-
Proinflammatory effects of tumour necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) on human gingival fibroblasts.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Dec;146(3):540-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03233.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17100776 Free PMC article.
-
TWEAKing tissue remodeling by a multifunctional cytokine: role of TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in health and disease.Cytokine. 2007 Oct;40(1):1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.09.007. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Cytokine. 2007. PMID: 17981048 Review.
-
TWEAK and Fn14: new molecular targets for cancer therapy?Cancer Lett. 2006 Apr 8;235(1):11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.03.048. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 15885893 Review.
Cited by
-
Controversies in TWEAK-Fn14 signaling in skeletal muscle atrophy and regeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Sep;77(17):3369-3381. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03495-x. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32200423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin 3 induces a distinctive pattern of cytokine and chemokine production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via selective signaling pathways.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jun;60(6):1604-14. doi: 10.1002/art.24574. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19479862 Free PMC article.
-
The TNFSF12/TWEAK Modulates Colonic Inflammatory Fibroblast Differentiation and Promotes Fibroblast-Monocyte Interactions.J Immunol. 2024 Jun 15;212(12):1958-1970. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300762. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38700420 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of TWEAK with Fn14 leads to the progression of fibrotic liver disease by directly modulating hepatic stellate cell proliferation.J Pathol. 2016 May;239(1):109-21. doi: 10.1002/path.4707. Epub 2016 Mar 29. J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26924336 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin Disrupts a Tnfrsf12a-Mediated Feed Forward Loop That Promotes Left Ventricular Hypertrophy.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022 Aug;36(4):619-632. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07190-2. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022. PMID: 33886003
References
-
- Campbell S, Michaelson J, Burkly L, Putterman C. The role of TWEAK/Fn14 in the pathogenesis of inflammation and systemic autoimmunity. Front Biosci. 2004;9:2273–2284. - PubMed
-
- Meighan-Mantha RL, Hsu DK, Guo Y, Brown SA, Feng SL, Peifley KA, Alberts GF, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, et al. The mitogen-inducible Fn14 gene encodes a type I transmembrane protein that modulates fibroblast adhesion and migration. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:33166–33176. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.46.33166. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

