Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications of the p53 family
- PMID: 16925948
- PMCID: PMC1601941
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.06439
Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications of the p53 family
Abstract
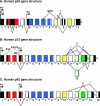
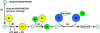
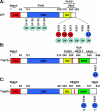
Regulation of p53 by the ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway has been studied considerably. Studies have also demonstrated that the ubiquitin-like proteins SUMO-1 and NEDD8 modify p53. Similarly, p63 and p73 are subject to regulation by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications, and perturbations of these pathways in the regulation of the p53 family have been implicated in tumorigenesis and developmental abnormalities. Here, we provide an overview of the current understanding of the regulation of the p53 family by covalent modification by ubiquitin, SUMO-1, and NEDD8.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of p53 by conjugation to the ubiquitin-like protein SUMO-1.EMBO J. 1999 Nov 15;18(22):6462-71. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.22.6462. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10562558 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-1 modification activates the transcriptional response of p53.EMBO J. 1999 Nov 15;18(22):6455-61. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.22.6455. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10562557 Free PMC article.
-
p53-Ubl fusions as models of ubiquitination, sumoylation and neddylation of p53.Cell Cycle. 2008 Aug 15;7(16):2519-28. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.16.6422. Epub 2008 Aug 9. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18719371
-
Regulation of the p53 pathway by ubiquitin and related proteins.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;42(10):1618-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.06.011. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20601087 Review.
-
Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins in protein regulation.Circ Res. 2007 May 11;100(9):1276-91. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000264500.11888.f0. Circ Res. 2007. PMID: 17495234 Review.
Cited by
-
DoUBLing up: ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteases in genome stability.Biochem J. 2024 Apr 10;481(7):515-545. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20230284. Biochem J. 2024. PMID: 38572758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular determinants for distinguishing between ubiquitin and NEDD8 by USP2.Sci Rep. 2017 May 23;7(1):2304. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02322-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28536428 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory feedback loop between TP73 and TRIM32.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Jul 4;4(7):e704. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.224. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23828567 Free PMC article.
-
UBE4B: a promising regulatory molecule in neuronal death and survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Dec 10;13(12):16865-79. doi: 10.3390/ijms131216865. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23222733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A microRNA-dependent program controls p53-independent survival and chemosensitivity in human and murine squamous cell carcinoma.J Clin Invest. 2011 Feb;121(2):809-20. doi: 10.1172/JCI43897. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21293058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang A, Kaghad M, Wang Y, Gillett E, Fleming MD, Dotsch V, Andrews NC, Caput D, McKeon F. p63, a p53 homolog at 3q27-29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol Cell. 1998;2:305–316. - PubMed
-
- Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan J-C, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Lelias J-M, Dumont X, et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell. 1997;90:809–819. - PubMed
-
- Jost CA, Marin MC, Kaelin WG., Jr p73 is a simian [correction of human] p53-related protein that can induce apoptosis. Nature. 1997;389:191–194. - PubMed
-
- Osada M, Ohba M, Kawahara C, Ishioka C, Kanamaru R, Katoh I, Ikawa Y, Nimura Y, Nakagawara A, Obinata M, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of human p51, which structurally and functionally resembles p53 [see comments] Nat Med. 1998;4:839–843. ([published erratum appears in Nat Med 1998;4(9):982]) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
