Brd4 links chromatin targeting to HPV transcriptional silencing
- PMID: 16921027
- PMCID: PMC1560413
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1448206
Brd4 links chromatin targeting to HPV transcriptional silencing
Abstract
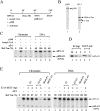
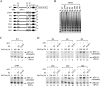
The E2 protein encoded by human papillomaviruses (HPVs) inhibits expression of the viral E6 oncoprotein, which, in turn, regulates p53 target gene transcription. To identify cellular proteins involved in E2-mediated transcriptional repression, we isolated an E2 complex from human cells conditionally expressing HPV-11 E2. Surprisingly, the double bromodomain-containing protein Brd4, which is implicated in cell cycle control and viral genome segregation, was found associated with E2 and conferred on E2 the ability to inhibit AP-1-dependent HPV chromatin transcription in an E2-binding site-specific manner as illustrated by in vitro reconstituted chromatin transcription experiments. Knockdown of Brd4 in human cells alleviates E2-mediated repression of HPV transcription. The E2-interacting domain at the extreme C terminus and the chromatin targeting activity of a bromodomain-containing region are both essential for the corepressor activity of Brd4. Interestingly, E2-Brd4 blocks the recruitment of TFIID and RNA polymerase II to the HPV E6 promoter region without inhibiting acetylation of nucleosomal histones H3 and H4, indicating an acetylation-dependent role of Brd4 in the recruitment of E2 for transcriptional silencing of HPV gene activity. Our finding that Brd4 is a component of the virus-assembled transcriptional silencing complex uncovers a novel function of Brd4 as a cellular cofactor modulating viral gene expression.
Figures

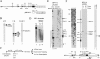



Similar articles
-
Abrogation of the Brd4-positive transcription elongation factor B complex by papillomavirus E2 protein contributes to viral oncogene repression.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(1):76-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01647-09. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19846528 Free PMC article.
-
The double bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor Brd4 and transcriptional regulation.J Biol Chem. 2007 May 4;282(18):13141-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R700001200. Epub 2007 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17329240 Review.
-
Chromatin adaptor Brd4 modulates E2 transcription activity and protein stability.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 30;284(5):2778-2786. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805835200. Epub 2008 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19038968 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide siRNA screen identifies SMCX, EP400, and Brd4 as E2-dependent regulators of human papillomavirus oncogene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3752-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914818107. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133580 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Brd4 in different steps of the papillomavirus life cycle.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.12.006. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27965149 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A proteomic approach to discover and compare interacting partners of papillomavirus E2 proteins from diverse phylogenetic groups.Proteomics. 2015 Jun;15(12):2038-50. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400613. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25758368 Free PMC article.
-
Early inhibition of BRD4 facilitates iPSC reprogramming via accelerating rDNA dynamic expression.BMC Biol. 2024 Sep 11;22(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01997-9. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39256730 Free PMC article.
-
Abrogation of the Brd4-positive transcription elongation factor B complex by papillomavirus E2 protein contributes to viral oncogene repression.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(1):76-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01647-09. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19846528 Free PMC article.
-
NCoR1 mediates papillomavirus E8;E2C transcriptional repression.J Virol. 2010 May;84(9):4451-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02390-09. Epub 2010 Feb 24. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20181716 Free PMC article.
-
The BRD3 ET domain recognizes a short peptide motif through a mechanism that is conserved across chromatin remodelers and transcriptional regulators.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 11;293(19):7160-7175. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000678. Epub 2018 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29567837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blachon S., Bellanger S., Demeret C., Thierry F. Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of high risk human papillomavirus E2 proteins induces apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:36088–36098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
