Antibody responses elicited in macaques immunized with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) SF162-derived gp140 envelope immunogens: comparison with those elicited during homologous simian/human immunodeficiency virus SHIVSF162P4 and heterologous HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 16912322
- PMCID: PMC1563892
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00956-06
Antibody responses elicited in macaques immunized with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) SF162-derived gp140 envelope immunogens: comparison with those elicited during homologous simian/human immunodeficiency virus SHIVSF162P4 and heterologous HIV-1 infection
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2007 Feb;81(3):1538
Abstract
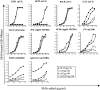
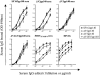
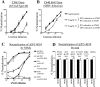
The antibody responses elicited in rhesus macaques immunized with soluble human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Env gp140 proteins derived from the R5-tropic HIV-1 SF162 virus were analyzed and compared to the broadly reactive neutralizing antibody responses elicited during chronic infection of a macaque with a simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) expressing the HIV-1 SF162 Env, SHIV(SF162P4), and humans infected with heterologous HIV-1 isolates. Four gp140 immunogens were evaluated: SF162gp140, DeltaV2gp140 (lacking the crown of the V2 loop), DeltaV3gp140 (lacking the crown of the V3 loop), and DeltaV2DeltaV3gp140 (lacking both the V2 and V3 loop crowns). SF162gp140 and DeltaV2gp140 have been previously evaluated by our group in a pilot study, but here, a more comprehensive analysis of their immunogenic properties was performed. All four gp140 immunogens elicited stronger anti-gp120 than anti-gp41 antibodies and potent homologous neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) that primarily targeted the first hypervariable region (V1 loop) of gp120, although SF162gp140 also elicited anti-V3 NAbs. Heterologous NAbs were elicited by SF162gp140 and DeltaV2gp140 but were weak in potency and narrow in specificity. No heterologous NAbs were elicited by DeltaV3gp140 or DeltaV2DeltaV3gp140. In contrast, the SHIV(SF162P4)-infected macaque and HIV-infected humans generated similar titers of anti-gp120 and anti-gp41 antibodies and NAbs of significant breadth against primary HIV-1 isolates, which did not target the V1 loop. The difference in V1 loop immunogenicity between soluble gp140 and virion-associated gp160 Env proteins derived from SF162 may be the basis for the observed difference in the breadth of neutralization in sera from the immunized and infected animals studied here.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunization with HIV-1 SF162-derived Envelope gp140 proteins does not protect macaques from heterologous simian-human immunodeficiency virus SHIV89.6P infection.Virology. 2006 Jun 5;349(2):276-89. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.01.043. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16527321
-
Changes in the immunogenic properties of soluble gp140 human immunodeficiency virus envelope constructs upon partial deletion of the second hypervariable region.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(4):2310-20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2310-2320.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12551968 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of an oligomeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope antigen to elicit neutralizing antibodies against primary HIV-1 isolates is improved following partial deletion of the second hypervariable region.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(12):5526-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.12.5526-5540.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11356960 Free PMC article.
-
Protection of neonatal macaques against experimental SHIV infection by human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies.Transfus Clin Biol. 2001 Aug;8(4):350-8. doi: 10.1016/s1246-7820(01)00187-2. Transfus Clin Biol. 2001. PMID: 11642027 Review.
-
Dissecting the humoral immune response to simian immunodeficiency virus: mechanisms of antibody-mediated virus neutralization.Immunol Res. 2006;36(1-3):51-60. doi: 10.1385/IR:36:1:51. Immunol Res. 2006. PMID: 17337766 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recombinant HIV envelope proteins fail to engage germline versions of anti-CD4bs bNAbs.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Jan;9(1):e1003106. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003106. Epub 2013 Jan 3. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23300456 Free PMC article.
-
Increased immunogenicity of HIV-1 p24 and gp120 following immunization with gp120/p24 fusion protein vaccine expressing alpha-gal epitopes.Vaccine. 2010 Feb 17;28(7):1758-65. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.12.015. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20034607 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing antibody responses to subtype B and C adjuvanted HIV envelope protein vaccination in rabbits.Virology. 2009 Apr 25;387(1):147-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.02.005. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19249806 Free PMC article.
-
Improved induction of antibodies against key neutralizing epitopes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 DNA prime-protein boost vaccination compared to gp120 protein-only vaccination.J Virol. 2008 Aug;82(15):7369-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00562-08. Epub 2008 May 21. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18495775 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env trimer immunization of macaques and impact of priming with viral vector or stabilized core protein.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(2):540-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01102-08. Epub 2008 Nov 12. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19004960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnett, S. W., S. Lu, I. Srivastava, S. Cherpelis, A. Gettie, J. Blanchard, S. Wang, I. Mboudjeka, L. Leung, Y. Lian, A. Fong, C. Buckner, A. Ly, S. Hilt, J. Ulmer, C. T. Wild, J. R. Mascola, and L. Stamatatos. 2001. The ability of an oligomeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope antigen to elicit neutralizing antibodies against primary HIV-1 isolates is improved following partial deletion of the second hypervariable region. J. Virol. 75:5526-5540. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beddows, S., S. Lister, R. Cheingsong, C. Bruck, and J. Weber. 1999. Comparison of the antibody repertoire generated in healthy volunteers following immunization with a monomeric recombinant gp120 construct derived from a CCR5/CXCR4-using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate with sera from naturally infected individuals. J. Virol. 73:1740-1745. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beddows, S., N. Schulke, M. Kirschner, K. Barnes, M. Franti, E. Michael, T. Ketas, R. W. Sanders, P. J. Maddon, W. C. Olson, and J. P. Moore. 2005. Evaluating the immunogenicity of a disulfide-stabilized, cleaved, trimeric form of the envelope glycoprotein complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 79:8812-8827. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., R. W. Sanders, B. Clas, N. Schuelke, A. Master, Y. Guo, F. Kajumo, D. J. Anselma, P. J. Maddon, W. C. Olson, and J. P. Moore. 2000. A recombinant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein complex stabilized by an intermolecular disulfide bond between the gp120 and gp41 subunits is an antigenic mimic of the trimeric virion-associated structure. J. Virol. 74:627-643. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., R. W. Sanders, A. Master, C. S. Cayanan, C. L. Wiley, L. Schiffner, B. Travis, S. Kuhmann, D. R. Burton, S. L. Hu, W. C. Olson, and J. P. Moore. 2002. Enhancing the proteolytic maturation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. 76:2606-2616. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

