Membrane-bound tomato mosaic virus replication proteins participate in RNA synthesis and are associated with host proteins in a pattern distinct from those that are not membrane bound
- PMID: 16912296
- PMCID: PMC1563852
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00545-06
Membrane-bound tomato mosaic virus replication proteins participate in RNA synthesis and are associated with host proteins in a pattern distinct from those that are not membrane bound
Abstract
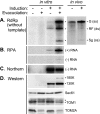
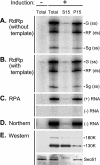
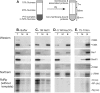
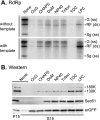
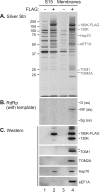
Extracts of vacuole-depleted, tomato mosaic virus (ToMV)-infected plant protoplasts contained an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) that utilized an endogenous template to synthesize ToMV-related positive-strand RNAs in a pattern similar to that observed in vivo. Despite the fact that only minor fractions of the ToMV 130- and 180-kDa replication proteins were associated with membranes, the RdRp activity was exclusively associated with membranes. A genome-sized, negative-strand RNA template was associated with membranes and was resistant to micrococcal nuclease unless treated with detergents. Non-membrane-bound replication proteins did not exhibit RdRp activity, even in the presence of ToMV RNA. While the non-membrane-bound replication proteins remained soluble after treatment with Triton X-100, the same treatment made the membrane-bound replication proteins in a form that precipitated upon low-speed centrifugation. On the other hand, the detergent lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) efficiently solubilized the membrane-bound replication proteins. Upon LPC treatment, the endogenous template-dependent RdRp activity was reduced and exogenous ToMV RNA template-dependent RdRp activity appeared instead. This activity, as well as the viral 130-kDa protein and the host proteins Hsp70, eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A (eEF1A), TOM1, and TOM2A copurified with FLAG-tagged viral 180-kDa protein from LPC-solubilized membranes. In contrast, Hsp70 and only small amounts of the 130-kDa protein and eEF1A copurified with FLAG-tagged non-membrane-bound 180-kDa protein. These results suggest that the viral replication proteins are associated with the intracellular membranes harboring TOM1 and TOM2A and that this association is important for RdRp activity. Self-association of the viral replication proteins and their association with other host proteins may also be important for RdRp activity.
Figures
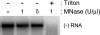

Similar articles
-
The resistance protein Tm-1 inhibits formation of a Tomato mosaic virus replication protein-host membrane protein complex.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(14):7933-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00743-13. Epub 2013 May 8. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23658455 Free PMC article.
-
A host small GTP-binding protein ARL8 plays crucial roles in tobamovirus RNA replication.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002409. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002409. Epub 2011 Dec 8. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22174675 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a ribonucleoprotein intermediate of tomato mosaic virus RNA replication complex formation.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(6):2584-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01921-06. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17108048 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of tomato mosaic virus RNA replication and its inhibition by the host resistance factor Tm-1.Curr Opin Virol. 2014 Dec;9:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.08.005. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Curr Opin Virol. 2014. PMID: 25212767 Review.
-
Replication of Tobamovirus RNA.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2016 Aug 4;54:55-78. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080615-100217. Epub 2016 May 25. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2016. PMID: 27296148 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in Subcellular Localization of Host Proteins Induced by Plant Viruses.Viruses. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):677. doi: 10.3390/v13040677. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33920930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Movement Protein Mediates Systemic Necrosis in Tomato Plants with Infection of Tomato Mosaic Virus.Viruses. 2023 Jan 4;15(1):157. doi: 10.3390/v15010157. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36680197 Free PMC article.
-
The eukaryotic elongation factor 1A is critical for genome replication of the paramyxovirus respiratory syncytial virus.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 5;9(12):e114447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114447. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25479059 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Roles of the Cis-acting Elements in Bamboo mosaic virus RNA Genome.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 13;8:645. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00645. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28450857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular chaperones and folding enzymes are vital contributors to membrane bound replication and movement complexes during plant RNA virus infection.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Dec 6;3:275. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00275. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 23230447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blumenthal, T., and G. G. Carmichael. 1979. RNA replication: function and structure of Qβ replicase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 48:525-548. - PubMed
-
- Browning, K. S., J. Humphreys, W. Hobbs, G. B. Smith, and J. M. Ravel. 1990. Determination of the amounts of the protein synthesis initiation and elongation factors in wheat germ. J. Biol. Chem. 265:17967-17973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

