Kinetics of the formation and dissociation of actin filament branches mediated by Arp2/3 complex
- PMID: 16905606
- PMCID: PMC1614474
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.106.080937
Kinetics of the formation and dissociation of actin filament branches mediated by Arp2/3 complex
Abstract
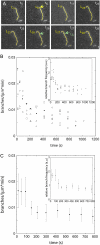
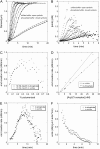
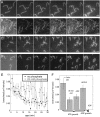
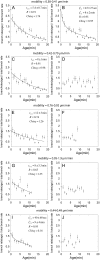
The actin filament network at the leading edge of motile cells relies on localized branching by Arp2/3 complex from "mother" filaments growing near the plasma membrane. The nucleotide bound to the mother filaments (ATP, ADP and phosphate, or ADP) may influence the branch dynamics. To determine the effect of the nucleotide bound to the subunits of the mother filament on the formation and stability of branches, we compared the time courses of actin polymerization in bulk samples measured using the fluorescence of pyrene actin with observations of single filaments by total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. Although the branch nucleation rate in bulk samples was nearly the same regardless of the nucleotide on the mother filaments, we observed fewer branches by microscopy on ADP-bound filaments than on ADP-P(i)-bound filaments. Observation of branches in the microscope depends on their binding to the slide. Since the probability that a branch binds to the slide is directly related to its lifetime, we used counts of branches to infer their rates of dissociation from mother filaments. We conclude that the nucleotide on the mother filament does not affect the initial branching event but that branches are an order of magnitude more stable on the sides of new ATP- or ADP-P(i) filaments than on ADP-actin filaments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structural basis of actin filament branching by the Arp2/3 complex.J Cell Biol. 2008 Mar 10;180(5):887-95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709092. Epub 2008 Mar 3. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18316411 Free PMC article.
-
Force and phosphate release from Arp2/3 complex promote dissociation of actin filament branches.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 16;117(24):13519-13528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911183117. Epub 2020 May 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32461373 Free PMC article.
-
The Arp2/3 complex nucleates actin filament branches from the sides of pre-existing filaments.Nat Cell Biol. 2001 Mar;3(3):306-10. doi: 10.1038/35060104. Nat Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11231582
-
Regulation of actin filament assembly by Arp2/3 complex and formins.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2007;36:451-77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.101936. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2007. PMID: 17477841 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms controlling actin filament dynamics in nonmuscle cells.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2000;29:545-76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.29.1.545. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2000. PMID: 10940259 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathway of actin filament branch formation by Arp2/3 complex revealed by single-molecule imaging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 22;110(4):1285-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211164110. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23292935 Free PMC article.
-
Coronin 1B antagonizes cortactin and remodels Arp2/3-containing actin branches in lamellipodia.Cell. 2008 Sep 5;134(5):828-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.054. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18775315 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of the cytoskeleton in autophagy.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2009 Aug;84(3):431-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2009.00082.x. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2009. PMID: 19659885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GMF is a cofilin homolog that binds Arp2/3 complex to stimulate filament debranching and inhibit actin nucleation.Curr Biol. 2010 May 11;20(9):861-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.026. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20362448 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila protein, Nausicaa, regulates lamellipodial actin dynamics in a Cortactin-dependent manner.Biol Open. 2019 Jun 17;8(6):bio038232. doi: 10.1242/bio.038232. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31164339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pollard, T. D., and G. G. Borisy. 2003. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell. 112:453–465. - PubMed
-
- Machesky, L. M. 1997. Cell motility: complex dynamics at the leading edge. Curr. Biol. 7:R164–R167. - PubMed
-
- Mullins, R. D., and M. D. Welch. 2002. Cellular control of actin nucleation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 18:247–288. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

