Onset of promiscuous gene expression in murine fetal thymus organ culture
- PMID: 16903901
- PMCID: PMC1819582
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02441.x
Onset of promiscuous gene expression in murine fetal thymus organ culture
Abstract
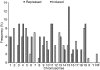
T-cell differentiation and induction of tolerance to self-antigens occurs mainly in the thymus. Thymic stromal cells, specifically medullary thymic epithelial cells, express a diverse set of genes encoding parenchymal organ-specific proteins. This phenomenon has been termed promiscuous gene expression (PGE) and has been implicated in preventing organ-specific autoimmunity by inducing T-cell tolerance to self antigens. Early thymopoiesis and the critical factors involved in T-cell differentiation can be reproduced in vitro by murine fetal thymus organ culture (FTOC), which mimics the natural thymic microenvironment. To evaluate the occurrence of PGE in FTOC, gene expression profiling during in vitro thymic development in BALB/c mice was performed using a set of nylon cDNA microarrays containing 9216 sequences. The statistical analysis of the microarray data (sam program) revealed the temporal repression and induction of 57 parenchymal and seven lymphoid organ-specific genes. Most of the genes analysed are repressed during early thymic development (15-17 days post-coitum). The expression of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene at 16 days post-coitum marks the onset of PGE. This precedes the induction of parenchymal organ genes during the late developmental phase at 20 days post-coitum. The mechanism of T-cell tolerance induction begins during fetal development and continues into adulthood. Our findings are significant because they show a fine demarcation of PGE onset, which plays a central role in induction of T-cell tolerance.
Figures
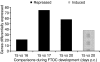


Similar articles
-
Promiscuous gene expression in the thymus: the root of central tolerance.Clin Dev Immunol. 2006 Jun-Dec;13(2-4):81-99. doi: 10.1080/17402520600877091. Clin Dev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17162352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybridization signatures of gamma-irradiated murine fetal thymus organ culture (FTOC) reveal modulation of genes associated with T-cell receptor V(D)J recombination and DNA repair.Mol Immunol. 2006 Feb;43(5):464-72. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2005.03.010. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Mol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16337489
-
Promiscuous gene expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells mirrors the peripheral self.Nat Immunol. 2001 Nov;2(11):1032-9. doi: 10.1038/ni723. Nat Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11600886
-
Evidence for a network transcriptional control of promiscuous gene expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells.Mol Immunol. 2009 Oct;46(16):3240-4. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.08.002. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19720399
-
Thymic T-cell tolerance of neuroendocrine functions: physiology and pathophysiology.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2001 Feb;47(1):179-88. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2001. PMID: 11292253 Review.
Cited by
-
Aire Downregulation Is Associated with Changes in the Posttranscriptional Control of Peripheral Tissue Antigens in Medullary Thymic Epithelial Cells.Front Immunol. 2016 Nov 23;7:526. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00526. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27933063 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty Years of AIRE.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 12;9:98. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00098. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29483906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble antigens from the neurotropic pathogen Angiostrongylus cantonensis directly induce thymus atrophy in a mouse model.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):48575-48590. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17836. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28548945 Free PMC article.
-
The Thymic Orchestration Involving Aire, miRNAs, and Cell-Cell Interactions during the Induction of Central Tolerance.Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 14;6:352. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00352. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26236310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential transcript profiles of MHC class Ib(Qa-1, Qa-2, and Qa-10) and Aire genes during the ontogeny of thymus and other tissues.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:159247. doi: 10.1155/2014/159247. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24829926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Junta CM, Passos GAS. Emergence of TCRαβ V (D) J recombination and transcription during thymus ontogeny of inbred mouse strains. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;187:67–72. - PubMed
-
- Macedo C, Junta CM, Passos GAS. Onset of T-cell receptor Vβ8.1 and Dβ2.1, V(D)J recombination during thymus development of inbred mouse strains. Immunol Lett. 1999;69:371–3. - PubMed
-
- Espanhol AR, Macedo C, Junta CM, et al. Gene expression profiling during thymus ontogeny and its association with TRVB8-DB2.1 rearrangements of inbred mouse strains. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;252:223–8. - PubMed
-
- Espanhol AR, Cardoso RS, Junta CM, Victorero G, Loriod B, Nguyen C, Passos GAS. Large scale gene expression analysis of CBA/J mouse strain fetal thymus using cDNA-array hybridizations. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;206:65–8. - PubMed
-
- Magalhães DA, Macedo C, Junta CM, et al. Hybridization signatures during thymus ontogeny reveals modulation of genes coding for T-cell signaling proteins. Mol Immunol. 2005;42:1043–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

