Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns3P] is generated at the plasma membrane by an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase: endogenous PtdIns3P can promote GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane
- PMID: 16880518
- PMCID: PMC1592800
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00203-06
Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns3P] is generated at the plasma membrane by an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase: endogenous PtdIns3P can promote GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane
Abstract
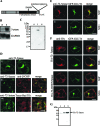
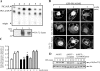
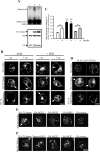
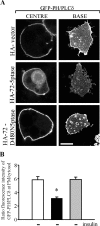
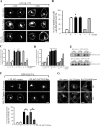
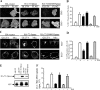
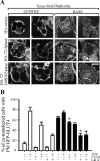
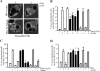
Exogenous delivery of carrier-linked phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns(3)P] to adipocytes promotes the trafficking, but not the insertion, of the glucose transporter GLUT4 into the plasma membrane. However, it is yet to be demonstrated if endogenous PtdIns(3)P regulates GLUT4 trafficking and, in addition, the metabolic pathways mediating plasma membrane PtdIns(3)P synthesis are uncharacterized. In unstimulated 3T3-L1 adipocytes, conditions under which PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 was not synthesized, ectopic expression of wild-type, but not catalytically inactive 72-kDa inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (72-5ptase), generated PtdIns(3)P at the plasma membrane. Immunoprecipitated 72-5ptase from adipocytes hydrolyzed PtdIns(3,5)P2, forming PtdIns(3)P. Overexpression of the 72-5ptase was used to functionally dissect the role of endogenous PtdIns(3)P in GLUT4 translocation and/or plasma membrane insertion. In unstimulated adipocytes wild type, but not catalytically inactive, 72-5ptase, promoted GLUT4 translocation and insertion into the plasma membrane but not glucose uptake. Overexpression of FLAG-2xFYVE/Hrs, which binds and sequesters PtdIns(3)P, blocked 72-5ptase-induced GLUT4 translocation. Actin monomer binding, using latrunculin A treatment, also blocked 72-5ptase-stimulated GLUT4 translocation. 72-5ptase expression promoted GLUT4 trafficking via a Rab11-dependent pathway but not by Rab5-mediated endocytosis. Therefore, endogenous PtdIns(3)P at the plasma membrane promotes GLUT4 translocation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An SH2 domain-containing 5' inositolphosphatase inhibits insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and growth factor-induced actin filament rearrangement.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1081-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1081. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891043 Free PMC article.
-
ArPIKfyve-PIKfyve interaction and role in insulin-regulated GLUT4 translocation and glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Jul 1;313(11):2404-16. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.03.024. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17475247 Free PMC article.
-
Role for a novel signaling intermediate, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, in insulin-regulated F-actin stress fiber breakdown and GLUT4 translocation.Endocrinology. 2004 Nov;145(11):4853-65. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0489. Epub 2004 Jul 29. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15284192
-
Regulation of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3/Akt signalling by inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Feb;44(1):240-52. doi: 10.1042/BST20150214. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 26862211 Review.
-
The role of the inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases in cellular function and human disease.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 1;419(1):29-49. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081673. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19272022 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoinositides are involved in control of the glucose-dependent growth resumption that follows the transition phase in Streptomyces lividans.J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(3):741-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00891-06. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17122350 Free PMC article.
-
INPP5E regulates phosphoinositide-dependent cilia transition zone function.J Cell Biol. 2017 Jan 2;216(1):247-263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201511055. Epub 2016 Dec 20. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27998989 Free PMC article.
-
The ciliary gene INPP5E confers dorsal telencephalic identity to human cortical organoids by negatively regulating Sonic hedgehog signaling.Cell Rep. 2022 May 17;39(7):110811. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110811. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35584663 Free PMC article.
-
Class II phosphoinositide 3-kinase C2alpha: what we learned so far.Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;2(2):168-182. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21968800 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositolphosphate phosphatase activities and cancer.J Lipid Res. 2016 Feb;57(2):176-92. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R059154. Epub 2015 Aug 24. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26302980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramoff, M., P. Magelhaes, and S. Ram. 2004. Image processing with Image J. Biophotonics Int. 11:36-42.
-
- Al-Hasani, H., C. S. Hinck, and S. W. Cushman. 1998. Endocytosis of the glucose transporter GLUT4 is mediated by the GTPase dynamin. J. Biol. Chem. 273:17504-17510. - PubMed
-
- Asano, T., A. Kanda, H. Katagiri, M. Nawano, T. Ogihara, K. Inukai, M. Anai, Y. Fukushima, Y. Yazaki, M. Kikuchi, R. Hooshmand-Rad, C. H. Heldin, Y. Oka, and M. Funaki. 2000. p110beta is up-regulated during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells and contributes to the highly insulin-responsive glucose transport activity. J. Biol. Chem. 275:17671-17676. - PubMed
-
- Asano, T., Y. Mochizuki, K. Matsumoto, T. Takenawa, and T. Endo. 1999. Pharbin, a novel inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, induces dendritic appearances in fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 261:188-195. - PubMed
-
- Backer, J. M. 2000. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases and the regulation of vesicular trafficking. Mol. Cell. Biol. Res. Commun. 3:193-204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
