A parA homolog selectively influences positioning of the large chromosome origin in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 16855253
- PMCID: PMC1540020
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00250-06
A parA homolog selectively influences positioning of the large chromosome origin in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
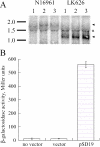
A Vibrio cholerae deletion mutant lacking VS2773, a parA partitioning gene homolog located in a parAB operon on the large chromosome, displays altered positioning of the large chromosome origin. Deletion of a second parA homolog on the large chromosome (VC2061) does not affect its origin positioning. The origin position of the small chromosome is unchanged by either or both of these deletions, suggesting that VC2773 function is specific to the replicon on which it is carried. VC2773 and VC2772 form a parABS system with inverted repeats found near the large chromosome origin.
Figures


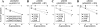
Similar articles
-
The chromosome partitioning proteins Soj (ParA) and Spo0J (ParB) contribute to accurate chromosome partitioning, separation of replicated sister origins, and regulation of replication initiation in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 2006 May;60(4):853-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05140.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16677298
-
Distinct segregation dynamics of the two Vibrio cholerae chromosomes.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jan;55(1):125-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04379.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15612922
-
ParABS systems of the four replicons of Burkholderia cenocepacia: new chromosome centromeres confer partition specificity.J Bacteriol. 2006 Feb;188(4):1489-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.4.1489-1496.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16452432 Free PMC article.
-
Management of multipartite genomes: the Vibrio cholerae model.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Dec;22:120-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.10.003. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25460805 Review.
-
Bacterial chromosome segregation by the ParABS system.Open Biol. 2020 Jun;10(6):200097. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200097. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32543349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The three vibrio cholerae chromosome II-encoded ParE toxins degrade chromosome I following loss of chromosome II.J Bacteriol. 2011 Feb;193(3):611-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01185-10. Epub 2010 Nov 29. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21115657 Free PMC article.
-
Centromere binding and evolution of chromosomal partition systems in the Burkholderiales.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jul;194(13):3426-36. doi: 10.1128/JB.00041-12. Epub 2012 Apr 20. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22522899 Free PMC article.
-
DNA motifs that sculpt the bacterial chromosome.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Jan;9(1):15-26. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2477. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21164534 Review.
-
Evidence for a DNA-relay mechanism in ParABS-mediated chromosome segregation.Elife. 2014 May 23;3:e02758. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02758. Elife. 2014. PMID: 24859756 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for two different regulatory mechanisms linking replication and segregation of vibrio cholerae chromosome II.PLoS Genet. 2013 Jun;9(6):e1003579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003579. Epub 2013 Jun 20. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23818869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clark, D., and O. Maaloe. 1967. DNA replication and the cell cycle in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 23:99-112.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

