HIV-1 Nef selectively activates Src family kinases Hck, Lyn, and c-Src through direct SH3 domain interaction
- PMID: 16849330
- PMCID: PMC2892265
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M601128200
HIV-1 Nef selectively activates Src family kinases Hck, Lyn, and c-Src through direct SH3 domain interaction
Abstract
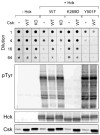
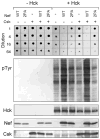
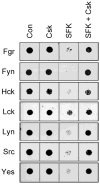
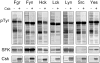
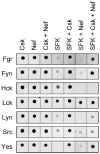
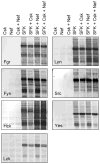
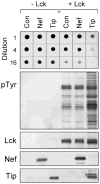
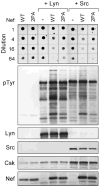
Nef is an HIV-1 virulence factor that promotes viral pathogenicity by altering host cell signaling pathways. Nef binds several members of the Src kinase family, and these interactions have been implicated in the pathogenesis of HIV/AIDS. However, the direct effect of Nef interaction on Src family kinase (SFK) regulation and activity has not been systematically addressed. We explored this issue using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a well defined model system for the study of SFK regulation. Previous studies have shown that ectopic expression of c-Src arrests yeast cell growth in a kinase-dependent manner. We expressed Fgr, Fyn, Hck, Lck, Lyn, and Yes as well as c-Src in yeast and found that each kinase was active and induced growth suppression. Co-expression of the negative regulatory kinase Csk suppressed SFK activity and reversed the growth-inhibitory effect. We then co-expressed each SFK with HIV-1 Nef in the presence of Csk. Nef strongly activated Hck, Lyn, and c-Src but did not detectably affect Fgr, Fyn, Lck, or Yes. Mutagenesis of the Nef PXXP motif essential for SH3 domain binding greatly reduced the effect of Nef on Hck, Lyn, and c-Src, suggesting that Nef activates these Src family members through allosteric displacement of intramolecular SH3-linker interactions. These data show that Nef selectively activates Hck, Lyn, and c-Src among SFKs, identifying these kinases as proximal effectors of Nef signaling and potential targets for anti-HIV drug discovery.
Figures
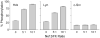
Similar articles
-
Affinity of Src family kinase SH3 domains for HIV Nef in vitro does not predict kinase activation by Nef in vivo.Biochemistry. 2000 Jan 25;39(3):489-95. doi: 10.1021/bi992504j. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10642173
-
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein binds the Src-related tyrosine kinase Lck SH2 domain through a novel phosphotyrosine independent mechanism.Virology. 1998 Aug 1;247(2):200-11. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9244. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9705913
-
Activation of STAT3 by the Src family kinase Hck requires a functional SH3 domain.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 22;277(47):45680-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204255200. Epub 2002 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12244095
-
Src family kinases: regulation of their activities, levels and identification of new pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1784(1):56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.08.012. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17905674 Review.
-
Interactions of the HIV/SIV pathogenicity factor Nef with SH3 domain-containing host cell proteins.Curr HIV Res. 2011 Oct;9(7):531-42. doi: 10.2174/157016211798842107. Curr HIV Res. 2011. PMID: 22103837 Review.
Cited by
-
Noncanonical binding of Lck to CD3ε promotes TCR signaling and CAR function.Nat Immunol. 2020 Aug;21(8):902-913. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0732-3. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32690949
-
Effector kinase coupling enables high-throughput screens for direct HIV-1 Nef antagonists with antiretroviral activity.Chem Biol. 2013 Jan 24;20(1):82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.11.005. Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23352142 Free PMC article.
-
Nef homodimers down-regulate SERINC5 by AP-2-mediated endocytosis to promote HIV-1 infectivity.J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 13;295(46):15540-15552. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014668. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32873704 Free PMC article.
-
Nef enhances HIV-1 replication and infectivity independently of SERINC5 in CEM T cells.Virology. 2023 Jan;578:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2022.12.008. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Virology. 2023. PMID: 36577173 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics reveal the essential role of linker motions in the function of cullin-RING E3 ligases.J Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 12;396(5):1508-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.022. Epub 2010 Jan 18. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20083119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fackler OT, Baur AS. Immunity. 2002;16:493–497. - PubMed
-
- Peter F. Immunity. 1998;9:433–437. - PubMed
-
- Joseph AM, Kumar M, Mitra D. Curr HIV Res. 2005;3:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Daniel MD, Kirchhoff F, Czajak SC, Sehgal PK, Desrosiers RC. Science. 1992;258:1938–1941. - PubMed
-
- Kestler HW, III, Ringler DJ, Mori K, Panicali DL, Sehgal PK, Daniel MD, Desrosiers RC. Cell. 1991;65:651–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

