Quaternary structure predictions of transmembrane proteins starting from the monomer: a docking-based approach
- PMID: 16836758
- PMCID: PMC1590055
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-340
Quaternary structure predictions of transmembrane proteins starting from the monomer: a docking-based approach
Abstract
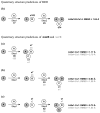
Background: We introduce a computational protocol for effective predictions of the supramolecular organization of integral transmembrane proteins, starting from the monomer. Despite the demonstrated constitutive and functional importance of supramolecular assemblies of transmembrane subunits or proteins, effective tools for structure predictions of such assemblies are still lacking. Our computational approach consists in rigid-body docking samplings, starting from the docking of two identical copies of a given monomer. Each docking run is followed by membrane topology filtering and cluster analysis. Prediction of the native oligomer is therefore accomplished by a number of progressive growing steps, each made of one docking run, filtering and cluster analysis. With this approach, knowledge about the oligomerization status of the protein is required neither for improving sampling nor for the filtering step. Furthermore, there are no size-limitations in the systems under study, which are not limited to the transmembrane domains but include also the water-soluble portions.
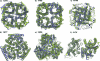
Results: Benchmarks of the approach were done on ten homo-oligomeric membrane proteins with known quaternary structure. For all these systems, predictions led to native-like quaternary structures, i.e. with Calpha-RMSDs lower than 2.5 A from the native oligomer, regardless of the resolution of the structural models.
Conclusion: Collectively, the results of this study emphasize the effectiveness of the prediction protocol that will be extensively challenged in quaternary structure predictions of other integral membrane proteins.
Figures

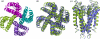
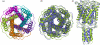
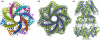

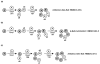
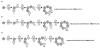
Similar articles
-
Membrane assembly of simple helix homo-oligomers studied via molecular dynamics simulations.Biophys J. 2007 Feb 1;92(3):854-63. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.095216. Epub 2006 Nov 3. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17085501 Free PMC article.
-
Structural modeling of protein interactions by analogy: application to PSD-95.PLoS Comput Biol. 2006 Nov 10;2(11):e153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020153. Epub 2006 Oct 4. PLoS Comput Biol. 2006. PMID: 17096593 Free PMC article.
-
Structure prediction of helical transmembrane proteins at two length scales.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2006 Apr;4(2):317-33. doi: 10.1142/s0219720006001965. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2006. PMID: 16819786
-
Protein complexes: structure prediction challenges for the 21st century.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Feb;15(1):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.01.012. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 15718128 Review.
-
Molecular simulation of protein aggregation.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007 Jan 1;96(1):1-8. doi: 10.1002/bit.21232. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007. PMID: 17136749 Review.
Cited by
-
Inactive and active states and supramolecular organization of GPCRs: insights from computational modeling.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2006 Jul-Aug;20(7-8):449-61. doi: 10.1007/s10822-006-9064-0. Epub 2006 Sep 29. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2006. PMID: 17009093 Review.
-
Functional rewiring of G protein-coupled receptor signaling in human labor.Cell Rep. 2022 Sep 6;40(10):111318. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111318. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36070698 Free PMC article.
-
Extension of a protein docking algorithm to membranes and applications to amyloid precursor protein dimerization.Proteins. 2015 Dec;83(12):2170-85. doi: 10.1002/prot.24934. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Proteins. 2015. PMID: 26404856 Free PMC article.
-
Computational study of the heterodimerization between mu and delta receptors.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2009 Jun;23(6):321-32. doi: 10.1007/s10822-009-9262-7. Epub 2009 Feb 13. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2009. PMID: 19214754
-
The dimerization interface of the glycoprotein Ibβ transmembrane domain corresponds to polar residues within a leucine zipper motif.Protein Sci. 2011 Nov;20(11):1814-23. doi: 10.1002/pro.713. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Protein Sci. 2011. PMID: 21830242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Membrane proteins of known 3D structure [http://blanco.biomol.uci.edu/Membrane_Proteins_xtal.html]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

