Insulin resistance and pancreatic beta cell failure
- PMID: 16823472
- PMCID: PMC1483164
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29189
Insulin resistance and pancreatic beta cell failure
Abstract
It is now well accepted that diabetes mellitus is one of the main threats to human health in the twenty-first century. The total number of people with diabetes worldwide was estimated at between 151 million and 171 million in 2000 and is projected to increase to 221 million in 2010 and to 366 million in 2030. Needless to say, the increase in the number of people with diabetes will be accompanied by an increase in the number of those with diabetic complications such as nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, and atherosclerosis. The global mortality attributable to diabetes in the year 2000 was estimated at 2.9 million deaths, a number that will also increase. Given that type 2 diabetes accounts for more than 90% of cases of diabetes worldwide, it is important that we understand the pathogenesis of this condition and develop new approaches to its prevention and treatment.
Figures
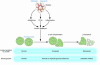
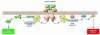
Similar articles
-
Role of islet amyloid in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(5-6):726-36. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.12.009. Epub 2006 Jan 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16459127 Review.
-
Insulin resistance, beta-cell function, and glucose tolerance in Brazilian adolescents with obesity or risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Complications. 2007 Mar-Apr;21(2):84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2005.11.006. J Diabetes Complications. 2007. PMID: 17331856
-
Beta-cell function and mass in type 2 diabetes.Dan Med Bull. 2009 Aug;56(3):153-64. Dan Med Bull. 2009. PMID: 19728971
-
The relation of insulin resistance syndromes to risk of cardiovascular disease.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2003;4 Suppl 6:S11-8. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2003. PMID: 14668699 Review.
-
Fate of the beta-cell in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes.J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2009 Sep-Oct;49 Suppl 1:S10-5. doi: 10.1331/JAPhA.2009.09076. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2009. PMID: 19801360 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin receptor endocytosis in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Jun;52(6):911-920. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0456-3. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32576931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipsin preserves beta cells in diabetic mice and associates with protection from type 2 diabetes in humans.Nat Med. 2019 Nov;25(11):1739-1747. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0610-4. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 31700183 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Apoptosis, Autophagy and Oxidative Stress in Pancreatic Islets Cells and Intestinal Epithelial Cells Isolated from Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS) Horses.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 8;19(10):3068. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103068. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30297648 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of obesity-induced metabolic and vascular dysfunctions.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2019 Mar 1;24(5):890-934. doi: 10.2741/4758. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2019. PMID: 30844720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Links between the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) recommended foods and disease management: A review in the light of modern superfoods.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018 Mar-Apr;12(2):61-69. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018. PMID: 29599697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson J.W., Kendall C.W., Jenkins D.J. Importance of weight management in type 2 diabetes: review with meta-analysis of clinical studies. . J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003;22:331–339. - PubMed
-
- Michael M.D., et al. Loss of insulin signaling in hepatocytes leads to severe insulin resistance and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Bruning J.C., et al. A muscle-specific insulin receptor knockout exhibits features of the metabolic syndrome of NIDDM without altering glucose tolerance. Mol. Cell. 1998;2:559–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

