HERC5 is an IFN-induced HECT-type E3 protein ligase that mediates type I IFN-induced ISGylation of protein targets
- PMID: 16815975
- PMCID: PMC1484417
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0600397103
HERC5 is an IFN-induced HECT-type E3 protein ligase that mediates type I IFN-induced ISGylation of protein targets
Abstract
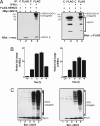
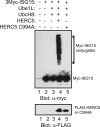
Type I IFNs induce the expression of IFN-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) and its conjugation to cellular targets. ISGylation is a multistep process involving IFN-inducible Ube1L, UbcH8, and a yet-to-be identified E3 ligase. Here we report the identification of an IFN-induced HECT-type E3 protein ligase, HERC5/Ceb1, which mediates ISGylation. We also defined a number of proteins modified by ISG15 after IFN triggering or HERC5 overexpression. A reduction in endogenous HERC5 by small interfering RNA inhibition blocks the IFN-induced ISG15 conjugation. Conversely, HERC5 coexpression with Ube1L and UbcH8 induces the ISG15 conjugation in vivo independent of IFN stimulation. A targeted substitution of Cys-994 to Ala in the HECT domain of HERC5 completely abrogates its E3 protein ligase activity. Therefore, this study demonstrates that HERC5/Ceb1 is involved in the conjugation of ISG15 to cellular proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
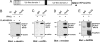
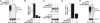
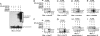
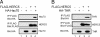
Similar articles
-
Herc5, an interferon-induced HECT E3 enzyme, is required for conjugation of ISG15 in human cells.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 17;281(7):4334-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512830200. Epub 2005 Dec 28. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407192
-
Identification and Herc5-mediated ISGylation of novel target proteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Sep 22;348(2):473-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.076. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16884686
-
HERC6 is the main E3 ligase for global ISG15 conjugation in mouse cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029870. Epub 2012 Jan 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22272257 Free PMC article.
-
HERC5 and the ISGylation Pathway: Critical Modulators of the Antiviral Immune Response.Viruses. 2021 Jun 9;13(6):1102. doi: 10.3390/v13061102. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34207696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ISG15 and immune diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 May;1802(5):485-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.02.006. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20153823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modification of BECN1 by ISG15 plays a crucial role in autophagy regulation by type I IFN/interferon.Autophagy. 2015 Apr 3;11(4):617-28. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1023982. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25906440 Free PMC article.
-
Fish HERC7: Phylogeny, Characterization, and Potential Implications for Antiviral Immunity in European Sea Bass.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 15;25(14):7751. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147751. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062994 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza Virus Host Restriction Factors: The ISGs and Non-ISGs.Pathogens. 2024 Jan 29;13(2):127. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13020127. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38392865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation and regulation of interferon-β in immune responses.Immunol Res. 2012 Sep;53(1-3):25-40. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8293-7. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22411096 Review.
-
Negative regulation of ISG15 E3 ligase EFP through its autoISGylation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Mar 2;354(1):321-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.210. Epub 2007 Jan 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17222803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Decker T., Muller M., Stockinger S. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005;5:675–687. - PubMed
-
- Perry A. K., Chen G., Zheng D., Tang H., Cheng G. Cell Res. 2005;15:407–422. - PubMed
-
- Smith P. L., Lombardi G., Foster G. R. Mol. Immunol. 2005;42:869–877. - PubMed
-
- Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:651–662. - PubMed
-
- Stark G. R., Kerr I. M., Williams B. R., Silverman R. H., Schreiber R. D. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

