EGFP-tagged core and linker histones diffuse via distinct mechanisms within living cells
- PMID: 16815908
- PMCID: PMC1557551
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.079343
EGFP-tagged core and linker histones diffuse via distinct mechanisms within living cells
Abstract
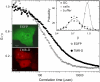
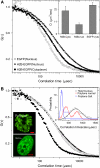
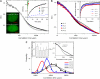
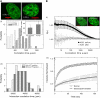
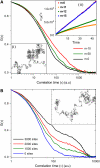
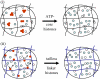
The effect of chromatin organization on EGFP-tagged histone protein dynamics within the cell nucleus has been probed using fluorescence correlation and recovery measurements on single living HeLa cells. Our studies reveal that free fraction of core-particle histones exist as multimers within the cell nucleus whereas the linker histones exist in monomeric forms. The multimeric state of core histones is found to be invariant across mammalian and polytene chromosomes and this is ATP dependent. In contrast, the dynamics of the linker histones exhibits two distinct diffusion timescales corresponding to its transient binding and unbinding to chromatin governed by the tail domain residues. Under conditions of chromatin condensation induced by apoptosis, the free multimeric fraction of core histones is found to become immobile, while the monomeric linker histone mobility is partially reduced. In addition, we observe differences in nuclear colocalization of linker and core particle histones. These results are validated through Brownian dynamics simulation of core and linker histone mobility. Our findings provide a framework to understand the coupling between the state of chromatin assembly and histone protein dynamics that is central to accessing regulatory sites on the genome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The core histone N termini function independently of linker histones during chromatin condensation.J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 24;275(47):37285-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006801200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10970897
-
HILS1 is a spermatid-specific linker histone H1-like protein implicated in chromatin remodeling during mammalian spermiogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Sep 2;100(18):10546-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1837812100. Epub 2003 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12920187 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin condensation fluctuations rather than steady-state predict chromatin accessibility.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):6184-6194. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz373. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31081027 Free PMC article.
-
What functions do linker histones provide?Mol Microbiol. 2004 Aug;53(3):771-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04195.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15255891 Review.
-
Analyses of linker histone--chromatin interactions in situ.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;84(4):427-36. doi: 10.1139/o06-071. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16936816 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamics of chromatin decondensation reveals the structural integrity of a mechanically prestressed nucleus.Biophys J. 2008 Sep 15;95(6):3028-35. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.132274. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18556763 Free PMC article.
-
Novel localization of formin mDia2: importin β-mediated delivery to and retention at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear envelope.Biol Open. 2015 Oct 30;4(11):1569-75. doi: 10.1242/bio.013649. Biol Open. 2015. PMID: 26519515 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy in the presence of immobile fluorophores.Biophys J. 2008 Mar 15;94(6):2349-60. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.115642. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18065480 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Delivery by Membrane Disruption: Mechanisms, Strategies, and Concepts.Chem Rev. 2018 Aug 22;118(16):7409-7531. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00678. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 30052023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for a transketolase-mediated metabolic checkpoint governing biotrophic growth in rice cells by the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Sep 4;10(9):e1004354. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004354. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25188286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spector, D. L. 2003. The dynamics of chromosome organization and gene regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72:573–608. - PubMed
-
- Schalch, T., S. Duda, D. F. Sargent, and T. J. Richmond. 2005. X-ray structure of a tetranucleosome and its implications for the chromatin fibre. Nature. 436:138–142. - PubMed
-
- Zlatanova, J., P. Caiafa, and K. van Holde. 2000. Linker histone binding and displacement: versatile mechanism for transcriptional regulation. FASEB J. 14:1697–1704. - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove, M. S., J. D. Boeke, and C. Wolberger. 2004. Regulated nucleosome mobility and the histone code. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11:1037–1043. - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein, T., and C. D. Allis. 2001. Translating the histone code. Science. 293:1074–1080. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

