Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 binding to endocytosis receptors of the low-density-lipoprotein receptor family by a peptide isolated from a phage display library
- PMID: 16813566
- PMCID: PMC1615895
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060533
Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 binding to endocytosis receptors of the low-density-lipoprotein receptor family by a peptide isolated from a phage display library
Abstract
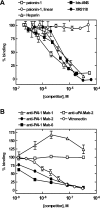
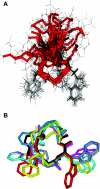
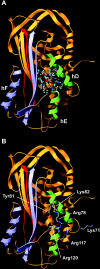
The functions of the serpin PAI-1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) are based on molecular interactions with its target proteases uPA and tPA (urokinase-type and tissue-type plasminogen activator respectively), with vitronectin and with endocytosis receptors of the low-density-lipoprotein family. Understanding the significance of these interactions would be facilitated by the ability to block them individually. Using phage display, we have identified the disulfide-constrained peptide motif CFGWC with affinity for natural human PAI-1. The three-dimensional structure of a peptide containing this motif (DVPCFGWCQDA) was determined by liquid-state NMR spectroscopy. A binding site in the so-called flexible joint region of PAI-1 was suggested by molecular modelling and validated through binding studies with various competitors and site-directed mutagenesis of PAI-1. The peptide with an N-terminal biotin inhibited the binding of the uPA-PAI-1 complex to the endocytosis receptors low-density-lipoprotein-receptor-related protein 1A (LRP-1A) and very-low-density-lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) in vitro and inhibited endocytosis of the uPA-PAI-1 complex in U937 cells. We conclude that the isolated peptide represents a novel approach to pharmacological interference with the functions of PAI-1 based on inhibition of one specific molecular interaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Binding of urokinase-type plasminogen activator-plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex to the endocytosis receptors alpha2-macroglobulin receptor/low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein and very-low-density lipoprotein receptor involves basic residues in the inhibitor.Biochem J. 1998 Jan 1;329 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):55-63. doi: 10.1042/bj3290055. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9405275 Free PMC article.
-
Binding areas of urokinase-type plasminogen activator-plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex for endocytosis receptors of the low-density lipoprotein receptor family, determined by site-directed mutagenesis.FEBS J. 2006 Nov;273(22):5143-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05511.x. Epub 2006 Oct 17. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 17042782
-
Analysis of a two-domain binding site for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator-plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex in low-density-lipoprotein-receptor-related protein.Biochem J. 2001 Jul 1;357(Pt 1):289-96. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3570289. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11415462 Free PMC article.
-
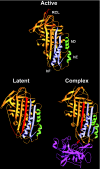
The molecular basis for anti-proteolytic and non-proteolytic functions of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1: roles of the reactive centre loop, the shutter region, the flexible joint region and the small serpin fragment.Biol Chem. 2002 Jan;383(1):21-36. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.003. Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11928815 Review.
-
Biochemical properties of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(4):1337-61. doi: 10.2741/3312. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273134 Review.
Cited by
-
Triglyceride Rich Lipoprotein -LPL-VLDL Receptor and Lp(a)-VLDL Receptor Pathways for Macrophage Foam Cell Formation.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017 Jun 1;24(6):552-559. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17004. Epub 2017 Apr 19. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017. PMID: 28428482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The High Affinity Binding Site on Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) for the Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein (LRP1) Is Composed of Four Basic Residues.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 8;291(2):800-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.688820. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26555266 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PAI-1 in Cardiovascular Disease: Structural Insights Into PAI-1 Functionality and Inhibition.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Dec 22;7:622473. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.622473. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 33415130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Review on Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Its (Patho)Physiological Role: To Target or Not to Target?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 8;22(5):2721. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052721. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 paradox in cancer: a mechanistic understanding.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019 Sep;38(3):483-492. doi: 10.1007/s10555-019-09806-4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019. PMID: 31734763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vaughan D. E. PAI-1 and atherothrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemostasis. 2005;3:1879–1883. - PubMed
-
- Durand M. K., Bødker J. S., Christensen A., Dupont D. M., Hansen M., Jensen J. K., Kjelgaard S., Mathiasen L., Pedersen K. E., Skeldal S., et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-I and tumour growth, invasion, and metastasis. Thromb. Haemostasis. 2004;91:438–449. - PubMed
-
- Behrendt N. The urokinase receptor (uPAR) and the uPAR-associated protein (uPARAP/Endo180): membrane proteins engaged in matrix turnover during tissue remodeling. Biol. Chem. 2004;385:103–136. - PubMed
-
- Gettins P. G. Serpin structure, mechanism, and function. Chem. Rev. 2002;102:4751–4804. - PubMed
-
- Egelund R., Rodenburg K. W., Andreasen P. A., Rasmussen M. S., Guldberg R. E., Petersen T. E. An ester bond linking a fragment of a serine proteinase to its serpin inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1998;37:6375–6379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

