Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson's models
- PMID: 16794039
- PMCID: PMC1983366
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1129462
Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson's models
Abstract
Alpha-synuclein (alphaSyn) misfolding is associated with several devastating neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's disease (PD). In yeast cells and in neurons alphaSyn accumulation is cytotoxic, but little is known about its normal function or pathobiology. The earliest defect following alphaSyn expression in yeast was a block in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi vesicular trafficking. In a genomewide screen, the largest class of toxicity modifiers were proteins functioning at this same step, including the Rab guanosine triphosphatase Ypt1p, which associated with cytoplasmic alphaSyn inclusions. Elevated expression of Rab1, the mammalian YPT1 homolog, protected against alphaSyn-induced dopaminergic neuron loss in animal models of PD. Thus, synucleinopathies may result from disruptions in basic cellular functions that interface with the unique biology of particular neurons to make them especially vulnerable.
Figures
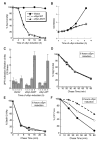
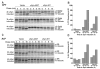
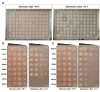
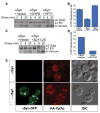
Similar articles
-
alpha-synuclein and Parkinson's disease: the first roadblock.J Cell Mol Med. 2006 Oct-Dec;10(4):837-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00528.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 17125588 Review.
-
The Parkinson's disease protein alpha-synuclein disrupts cellular Rab homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 8;105(1):145-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710685105. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18162536 Free PMC article.
-
Rab1A over-expression prevents Golgi apparatus fragmentation and partially corrects motor deficits in an alpha-synuclein based rat model of Parkinson's disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2011;1(4):373-87. doi: 10.3233/JPD-2011-11058. J Parkinsons Dis. 2011. PMID: 23939344
-
Alpha-synuclein-induced aggregation of cytoplasmic vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Mar;19(3):1093-103. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-08-0827. Epub 2008 Jan 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18172022 Free PMC article.
-
Rescuing defective vesicular trafficking protects against alpha-synuclein toxicity in cellular and animal models of Parkinson's disease.ACS Chem Biol. 2006 Aug 22;1(7):420-4. doi: 10.1021/cb600331e. ACS Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 17168518 Review.
Cited by
-
Gaucher-Associated Parkinsonism.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Aug;35(6):755-61. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0176-8. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25820783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Protein Palmitoylation as Disease Mechanism in Neurodegenerative Disorders.J Neurosci. 2024 Oct 2;44(40):e1225242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1225-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39358031 Review.
-
shRNA-Based Screen Identifies Endocytic Recycling Pathway Components That Act as Genetic Modifiers of Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation, Secretion and Toxicity.PLoS Genet. 2016 Apr 28;12(4):e1005995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005995. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27123591 Free PMC article.
-
DEAD-box RNA helicase Dbp4/DDX10 is an enhancer of α-synuclein toxicity and oligomerization.PLoS Genet. 2021 Mar 3;17(3):e1009407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009407. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33657088 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of RNA lariat debranching enzyme suppresses TDP-43 toxicity in ALS disease models.Nat Genet. 2012 Dec;44(12):1302-9. doi: 10.1038/ng.2434. Epub 2012 Oct 28. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 23104007 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

