Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia
- PMID: 16778145
- PMCID: PMC1895575
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-010777
Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia
Abstract
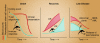
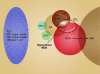
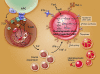
Aplastic anemia, an unusual hematologic disease, is the paradigm of the human bone marrow failure syndromes. Almost universally fatal just a few decades ago, aplastic anemia can now be cured or ameliorated by stem-cell transplantation or immunosuppressive drug therapy. The pathophysiology is immune mediated in most cases, with activated type 1 cytotoxic T cells implicated. The molecular basis of the aberrant immune response and deficiencies in hematopoietic cells is now being defined genetically; examples are telomere repair gene mutations in the target cells and dysregulated T-cell activation pathways. Immunosuppression with antithymocyte globulins and cyclosporine is effective at restoring blood-cell production in the majority of patients, but relapse and especially evolution of clonal hematologic diseases remain problematic. Allogeneic stem-cell transplant from histocompatible sibling donors is curative in the great majority of young patients with severe aplastic anemia; the major challenges are extending the benefits of transplantation to patients who are older or who lack family donors. Recent results with alternative sources of stem cells and a variety of conditioning regimens to achieve their engraftment have been promising, with survival in small pediatric case series rivaling conventional transplantation results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Idiopathic Aplastic Anemia in Children and Adults: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Management - A Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020;21(13):1282-1288. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666191210141426. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31820683 Review.
-
Acquired aplastic anemia.Ann Intern Med. 2002 Apr 2;136(7):534-46. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-7-200204020-00011. Ann Intern Med. 2002. PMID: 11926789 Review.
-
Aplastic anemia.Curr Opin Hematol. 2008 May;15(3):162-8. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3282fa7470. Curr Opin Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18391779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunosuppressive treatment of acquired aplastic anemia and immune-mediated bone marrow failure syndromes.Int J Hematol. 2002 Feb;75(2):129-40. doi: 10.1007/BF02982017. Int J Hematol. 2002. PMID: 11939258 Review.
-
Severe aplastic anemia and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.AACN Clin Issues. 2002 May;13(2):169-91. doi: 10.1097/00044067-200205000-00004. AACN Clin Issues. 2002. PMID: 12011591 Review.
Cited by
-
Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Mechanistic and Clinical Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 14;22(6):2954. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062954. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33799477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-dose Cyclophosphamide is Effective Therapy for Pediatric Severe Aplastic Anemia.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2016 Nov;38(8):627-635. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000647. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27467367 Free PMC article.
-
Model-Based Determination of Effective Blood Concentrations of Cyclosporine for Neutrophil Response in the Treatment of Severe Aplastic Anemia in Children.AAPS J. 2015 Sep;17(5):1157-67. doi: 10.1208/s12248-015-9779-8. Epub 2015 May 15. AAPS J. 2015. PMID: 25975616 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of heterozygosity in 7q myeloid disorders: clinical associations and genomic pathogenesis.Blood. 2012 Jun 21;119(25):6109-17. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-397620. Epub 2012 May 2. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22553315 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of 172 children with severe aplastic anemia treated with rabbit antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine.Ann Hematol. 2021 Jan;100(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-04296-9. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Ann Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33033910
References
-
- Young NS. Aplastic anemia. In: Young NS, ed. The Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders; 2000: 1-46.
-
- Kojima S, Nakao S, Tomonaga M, et al. Consensus conference on the treatment of aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol. 2000;72: 118-123. - PubMed
-
- Marsh JCW. Management of acquired aplastic anaemia. Blood Rev. 2005;19: 143-151. - PubMed
-
- Nakao S, Feng X, Sugimori C. Immune pathophysiology of aplastic anemia. Intl J Hematol. 2005;82: 196-200. - PubMed
-
- Young NS. Acquired aplastic anemia. In: Young NS, Gerson SL, High K, eds. Clinical Hematology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2006: 136-157.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

