Dicer-2 and R2D2 coordinately bind siRNA to promote assembly of the siRISC complexes
- PMID: 16775303
- PMCID: PMC1524895
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.101606
Dicer-2 and R2D2 coordinately bind siRNA to promote assembly of the siRISC complexes
Abstract
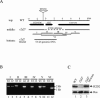
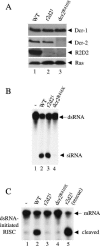
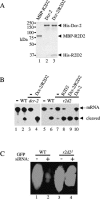
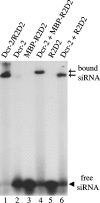
In Drosophila melanogaster, the Dicer-2/R2D2 complex initiates RNA interference (RNAi) by processing long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) into small interfering RNA (siRNA). Recent biochemical studies suggest that the Dcr-2/R2D2 complex also facilitates incorporation of siRNA into the RNA-induced silencing complex (siRISC). Here we present genetic evidence that R2D2 and Dcr-2 are both required for loading siRNA onto the siRISC complex. Consistent with this, only the Dcr-2/R2D2 complex, but neither Dcr-2 nor R2D2 alone, can efficiently interact with duplex siRNA. Furthermore, both dsRNA-binding domains of R2D2 are critical for binding to siRNA and promoting assembly of the siRISC complexes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
R2D2, a bridge between the initiation and effector steps of the Drosophila RNAi pathway.Science. 2003 Sep 26;301(5641):1921-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1088710. Science. 2003. PMID: 14512631
-
Dicer-1, but not Loquacious, is critical for assembly of miRNA-induced silencing complexes.RNA. 2007 Dec;13(12):2324-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.723707. Epub 2007 Oct 10. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17928574 Free PMC article.
-
TAF11 Assembles the RISC Loading Complex to Enhance RNAi Efficiency.Mol Cell. 2015 Sep 3;59(5):807-18. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26257286 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Loquacious speaks out.Curr Biol. 2005 Aug 9;15(15):R603-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.044. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16085484 Review.
-
The RNAi pathway initiated by Dicer-2 in Drosophila.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:39-44. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.008. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381278 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient kinetic studies of the antiviral Drosophila Dicer-2 reveal roles of ATP in self-nonself discrimination.Elife. 2021 Mar 31;10:e65810. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65810. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33787495 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila Dicer-1 Partner Loquacious Enhances miRNA Processing from Hairpins with Unstable Structures at the Dicing Site.Cell Rep. 2016 May 24;15(8):1795-808. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.059. Epub 2016 May 12. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27184838 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer's Helicase Domain: A Meeting Place for Regulatory Proteins.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2019;84:185-193. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2019.84.039750. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2019. PMID: 32179591 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs regulate Aedes aegypti vector competence for Zika virus and reproduction.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jun 15;19(6):e1011440. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011440. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37319296 Free PMC article.
-
A Tetrahymena Hsp90 co-chaperone promotes siRNA loading by ATP-dependent and ATP-independent mechanisms.EMBO J. 2015 Feb 12;34(4):559-77. doi: 10.15252/embj.201490062. Epub 2015 Jan 14. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25588944 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
