Dose-dependent Smad1, Smad5 and Smad8 signaling in the early mouse embryo
- PMID: 16765933
- PMCID: PMC7116376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.04.442
Dose-dependent Smad1, Smad5 and Smad8 signaling in the early mouse embryo
Abstract
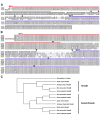
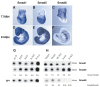
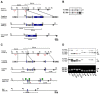
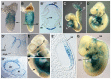
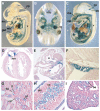
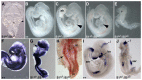
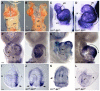
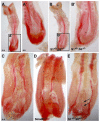
Three closely related mammalian R-Smads, namely Smad1, Smad5 and Smad8, are activated by BMP receptors. Here we have taken a genetic approach to further dissect their possibly unique and/or shared roles during early mouse development. A Smad8.LacZ reporter allele was created to visualize Smad8 expression domains. Smad8 is initially expressed only in the visceral yolk sac (VYS) endoderm and shows a highly restricted pattern of expression in the embryo proper at later stages. In addition, Smad8 conditional and null alleles were engineered. All alleles clearly demonstrate that adult Smad8 homozygous mutants are viable and fertile. To elucidate gene dosage effects, we manipulated expression ratios of the three BMP R-Smads. Smad8 homozygotes also lacking one copy of Smad1 or Smad5 did not exhibit overt phenotypes, and the tissue disturbances seen in Smad1 or Smad5 null embryos were not exacerbated in the absence of Smad8. However, we discovered a profound genetic interaction between Smad1 and Smad5. Thus, as for Smad1 and Smad5 mutant embryos, Smad1+/-:Smad5+/- double heterozygotes die by E10.5 and display defects in allantois morphogenesis, cardiac looping and primordial germ cell (PGC) specification. These experiments demonstrate for the first time that Smad1 and Smad5 function cooperatively to govern BMP target gene expression in the early mammalian embryo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BMP canonical Smad signaling through Smad1 and Smad5 is required for endochondral bone formation.Development. 2009 Apr;136(7):1093-104. doi: 10.1242/dev.029926. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Development. 2009. PMID: 19224984 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of Hepatocyte Smad1, Smad5, and Smad8 Causes Severe Tissue Iron Loading and Liver Fibrosis in Mice.Hepatology. 2019 Dec;70(6):1986-2002. doi: 10.1002/hep.30780. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 31127639 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating positional information at the level of Smad1/5/8.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008 Aug;18(4):304-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2008.06.001. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008. PMID: 18590818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse embryos lacking Smad1 signals display defects in extra-embryonic tissues and germ cell formation.Development. 2001 Sep;128(18):3609-21. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.18.3609. Development. 2001. PMID: 11566864
-
Integration of BMP and Wnt signaling via vertebrate Smad1/5/8 and Drosophila Mad.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009 Oct-Dec;20(5-6):357-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.10.017. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009. PMID: 19896409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid follicle development requires Smad1/5- and endothelial cell-dependent basement membrane assembly.Development. 2016 Jun 1;143(11):1958-70. doi: 10.1242/dev.134171. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Development. 2016. PMID: 27068110 Free PMC article.
-
Smad1 and Smad5 differentially regulate embryonic hematopoiesis.Blood. 2007 Dec 1;110(12):3881-90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-04-085753. Epub 2007 Aug 29. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17761518 Free PMC article.
-
BMP canonical Smad signaling through Smad1 and Smad5 is required for endochondral bone formation.Development. 2009 Apr;136(7):1093-104. doi: 10.1242/dev.029926. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Development. 2009. PMID: 19224984 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of TJP1 disrupts gastrulation patterning and increases differentiation toward the germ cell lineage in human pluripotent stem cells.Dev Cell. 2023 Aug 21;58(16):1477-1488.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.05.019. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Dev Cell. 2023. PMID: 37354899 Free PMC article.
-
Rnf165/Ark2C enhances BMP-Smad signaling to mediate motor axon extension.PLoS Biol. 2013;11(4):e1001538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001538. Epub 2013 Apr 16. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 23610558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki H, Fujii M, Imamura T, Yagi K, Takehara K, Kato M, Miyazono K. Synergistic effects of different bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors on alkaline phosphatase induction. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:1483–1489. - PubMed
-
- Biben C, Harvey RP. Homeodomain factor Nkx2-5 controls left/right asymmetric expression of bHLH gene eHand during murine heart development. Genes Dev. 1997;11:1357–1369. - PubMed
-
- Brennan J, Lu CC, Norris DP, Rodriguez TA, Beddington RS, Robertson EJ. Nodal signalling in the epiblast patterns the early mouse embryo. Nature. 2001;411:965–969. - PubMed
-
- Chang H, Matzuk MM. Smad5 is required for mouse primordial germ cell development. Mech Dev. 2001;104:61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

