A constitutively expressed, truncated umuDC operon regulates the recA-dependent DNA damage induction of a gene in Acinetobacter baylyi strain ADP1
- PMID: 16751513
- PMCID: PMC1489636
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02774-05
A constitutively expressed, truncated umuDC operon regulates the recA-dependent DNA damage induction of a gene in Acinetobacter baylyi strain ADP1
Abstract
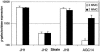
In response to environmentally caused DNA damage, SOS genes are up-regulated due to RecA-mediated relief of LexA repression. In Escherichia coli, the SOS umuDC operon is required for DNA damage checkpoint functions and for replicating damaged DNA in the error-prone process called SOS mutagenesis. In the model soil bacterium Acinetobacter baylyi strain ADP1, however, the content, regulation, and function of the umuDC operon are unusual. The umuC gene is incomplete, and a remnant of an ISEhe3-like transposase has replaced the middle 57% of the umuC coding region. The umuD open reading frame is intact, but it is 1.5 times the size of other umuD genes and has an extra 5' region that lacks homology to known umuD genes. Analysis of a umuD::lacZ fusion showed that umuD was expressed at very high levels in both the absence and presence of mitomycin C and that this expression was not affected in a recA-deficient background. The umuD mutation did not affect the growth rate or survival after UV-induced DNA damage. However, the UmuD-like protein found in ADP1 (UmuDAb) was required for induction of an adjacent DNA damage-inducible gene, ddrR. The umuD mutation specifically reduced the DNA damage induction of the RecA-dependent DNA damage-inducible ddrR locus by 83% (from 12.9-fold to 2.3-fold induction), but it did not affect the 33.9-fold induction of benA, an unrelated benzoate degradation gene. These data suggest that the response of the ADP1 umuDC operon to DNA damage is unusual and that UmuDAb specifically regulates the expression of at least one DNA damage-inducible gene.
Figures
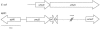

Similar articles
-
UmuDAb: An Error-Prone Polymerase Accessory Homolog Whose N-Terminal Domain Is Required for Repression of DNA Damage Inducible Gene Expression in Acinetobacter baylyi.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 24;11(3):e0152013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152013. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27010837 Free PMC article.
-
Prophage induction and differential RecA and UmuDAb transcriptome regulation in the DNA damage responses of Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter baylyi.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 7;9(4):e93861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093861. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24709747 Free PMC article.
-
The Acinetobacter regulatory UmuDAb protein cleaves in response to DNA damage with chimeric LexA/UmuD characteristics.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012 Sep;334(1):57-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02618.x. Epub 2012 Jul 5. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22697494 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analyses of cellular functions required for UV mutagenesis in Escherichia coli.Basic Life Sci. 1990;52:269-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9561-8_22. Basic Life Sci. 1990. PMID: 2183772 Review.
-
A new model for SOS-induced mutagenesis: how RecA protein activates DNA polymerase V.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Jun;45(3):171-84. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.480968. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20441441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Regulation of LexA on UV-Induced SOS Response in Myxococcus xanthus Based on Transcriptome Analysis.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 28;31(7):912-920. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2103.03047. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34024894 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a DNA-damage-inducible regulon in Acinetobacter baumannii.J Bacteriol. 2013 Dec;195(24):5577-82. doi: 10.1128/JB.00853-13. Epub 2013 Oct 11. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 24123815 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of phenotypic subpopulations in response to ciprofloxacin treatment in Acinetobacter baumannii.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Apr;92(1):138-52. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12541. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24612352 Free PMC article.
-
A corepressor participates in LexA-independent regulation of error-prone polymerases in Acinetobacter.Microbiology (Reading). 2020 Feb;166(2):212-226. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000866. Microbiology (Reading). 2020. PMID: 31687925 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genome analysis of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Clavibacter strains reveals adaptations to their lifestyle.BMC Genomics. 2014 May 22;15(1):392. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-392. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24885539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson, S. G., A. Zomorodipour, J. O. Andersson, T. Sicheritz-Ponten, U. C. Alsmark, R. M. Podowski, A. K. Naslund, A. S. Eriksson, H. H. Winkler, and C. G. Kurland. 1998. The genome sequence of Rickettsia prowazekii and the origin of mitochondria. Nature 396:133-140. - PubMed
-
- Barbe, V., D. Vallenet, N. Fonknechten, A. Kreimeyer, S. Oztas, L. Labarre, S. Cruveiller, C. Robert, S. Duprat, P. Wincker, L. N. Ornston, J. Weissenbach, P. Marliere, G. N. Cohen, and C. Medigue. 2004. Unique features revealed by the genome sequence of Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1, a versatile and naturally transformation competent bacterium. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:5766-5779. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Battista, J. R., T. Nohmi, C. E. Donnelly, and G. C. Walker. 1990. Genetic analyses of cellular functions required for UV mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Basic Life Sci. 52:269-275. - PubMed
-
- Berenstein, D. 1987. UV-inducible DNA repair in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Mutat. Res. 183:219-224. - PubMed
-
- Bonacossa de Almeida, C., G. Coste, S. Sommer, and A. Bailone. 2002. Quantification of RecA protein in Deinococcus radiodurans reveals involvement of RecA, but not LexA, in its regulation. Mol. Genet. Genomics 268:28-41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

