Molecular dissection of Rab11 binding from coiled-coil formation in the Rab11-FIP2 C-terminal domain
- PMID: 16734419
- PMCID: PMC2518868
- DOI: 10.1021/bi052655o
Molecular dissection of Rab11 binding from coiled-coil formation in the Rab11-FIP2 C-terminal domain
Abstract
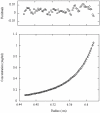
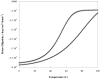
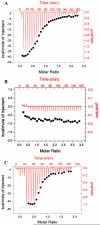
The Rab11-family interacting protein (Rab11-FIP) group of effector proteins contain a highly conserved region in their C-termini that bind the GTPase, Rab11. Rab11 belongs to the largest family of small GTPases and is believed to regulate vesicle docking with target membranes and vesicle fusion. The amino acid sequence of the Rab11-FIP proteins predicts coiled-coil formation in the conserved C-terminal domain. In this study on Rab11-FIP2, we found experimental evidence for the coiled-coil and then defined the minimal structured core using limited proteolysis. We also showed that the Rab11-FIP2 coiled-coil domain forms a parallel homodimer in solution using cross-linking and mutagenesis and sedimentation equilibrium experiments. Various constructs representing the C-terminal domain of Rab11-FIP2 were characterized by circular dichroism, and their affinity with Rab11 was measured using isothermal titration calorimetry. The longest construct was both well-structured and bound Rab11. A construct truncated at the N-terminus was poorly structured but retained the same affinity for binding to Rab11. Conformational changes were also demonstrated upon complex formation between Rab11 and Rab11-FIP2. A construct truncated at the C-terminus, which was the minimal coiled-coil domain defined by limited proteolysis, did not retain the ability to interact with Rab11, although it was as well-structured as the longer peptide. These data show that coiled-coil formation and Rab11 binding are separable functions of the C-terminal domain of Rab11-FIP2. The dissection of Rab11 binding from the formation of defined structure in a coiled-coil provides a potential mechanism for regulating Rab11-dependent endosomal trafficking.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Disorder and structure in the Rab11 binding domain of Rab11 family interacting protein 2.Biochemistry. 2009 Jan 27;48(3):549-57. doi: 10.1021/bi8020197. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19119858 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of rab11 in complex with rab11 family interacting protein 2.Structure. 2006 Aug;14(8):1273-83. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2006.06.010. Structure. 2006. PMID: 16905101
-
Structural and functional analysis of FIP2 binding to the endosome-localised Rab25 GTPase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1834(12):2679-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.09.005. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24056041
-
The dynamic Rab11-FIPs.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Oct;37(Pt 5):1032-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0371032. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19754446 Review.
-
Rabs, Rips, FIPs, and endocytic membrane traffic.ScientificWorldJournal. 2003 Sep 15;3:870-80. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2003.69. ScientificWorldJournal. 2003. PMID: 14532427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rab11-FIP2 interaction with MYO5B regulates movement of Rab11a-containing recycling vesicles.Traffic. 2014 Mar;15(3):292-308. doi: 10.1111/tra.12146. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Traffic. 2014. PMID: 24372966 Free PMC article.
-
Disorder and structure in the Rab11 binding domain of Rab11 family interacting protein 2.Biochemistry. 2009 Jan 27;48(3):549-57. doi: 10.1021/bi8020197. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19119858 Free PMC article.
-
RAB11A and RAB11B control mitotic spindle function in intestinal epithelial progenitor cells.EMBO Rep. 2023 Sep 6;24(9):e56240. doi: 10.15252/embr.202256240. Epub 2023 Jul 10. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37424454 Free PMC article.
-
The Rab11-family interacting proteins reveal selective interaction of mammalian recycling endosomes with the Toxoplasma parasitophorous vacuole in a Rab11- and Arf6-dependent manner.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 May 1;33(5):ar34. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-06-0284. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35274991 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the APPL1 BAR-PH domain and characterization of its interaction with Rab5.EMBO J. 2007 Jul 25;26(14):3484-93. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601771. Epub 2007 Jun 21. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17581628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zerial M, McBride H. Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Kumar R, Navarre J, Casanova JE, Goldenring JR. Regulation of vesicle trafficking in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells by Rab11a and Rab25. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:29138–29146. - PubMed
-
- Prekeris R, Klumperman J, Scheller RH. A Rab11/Rip11 protein complex regulates apical membrane trafficking via recycling endosomes. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:1437–1448. - PubMed
-
- Hales CM, Griner R, Hobdy-Henderson KC, Dorn MC, Hardy D, Kumar R, Navarre J, Chan EK, Lapierre LA, Goldenring JR. Identification and characterization of a family of Rab11-interacting proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:39067–39075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

