High potency silencing by single-stranded boranophosphate siRNA
- PMID: 16717282
- PMCID: PMC1464415
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl339
High potency silencing by single-stranded boranophosphate siRNA
Abstract
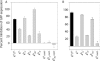
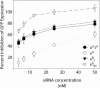
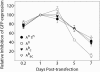
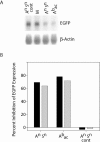
In RNA interference (RNAi), double-stranded short interfering RNA (ds-siRNA) inhibits expression from complementary mRNAs. Recently, it was demonstrated that short, single-stranded antisense RNA (ss-siRNA) can also induce RNAi. While ss-siRNA may offer several advantages in both clinical and research applications, its overall poor activity compared with ds-siRNA has prevented its widespread use. In contrast to the poor gene silencing activity of native ss-siRNA, we found that the silencing activity of boranophosphate-modified ss-siRNA is comparable with that of unmodified ds-siRNA. Boranophosphate ss-siRNA has excellent maximum silencing activity and is highly effective at low concentrations. The silencing activity of boranophosphate ss-siRNA is also durable, with significant silencing up to 1 week after transfection. Thus, we have demonstrated that boranophosphate-modified ss-siRNA can silence gene expression as well as native ds-siRNA, suggesting that boranophosphate-modified ss-siRNAs should be investigated as a potential new class of therapeutic agents.
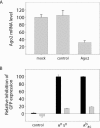
Figures


Similar articles
-
RNA interference using boranophosphate siRNAs: structure-activity relationships.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Nov 15;32(20):5991-6000. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh936. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15545637 Free PMC article.
-
Small interfering RNAs containing full 2'-O-methylribonucleotide-modified sense strands display Argonaute2/eIF2C2-dependent activity.RNA. 2006 Jan;12(1):163-76. doi: 10.1261/rna.2150806. Epub 2005 Nov 21. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16301602 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of metabolically stable 5'-phosphate analogs that support single-stranded siRNA activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 31;43(6):2993-3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv162. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25753666 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of chemically modified siRNA: Recent trends.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017 Nov;90(5):665-678. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12993. Epub 2017 May 16. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017. PMID: 28378934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical modification of siRNA.Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2009 Dec;Chapter 16:Unit 16.3. doi: 10.1002/0471142700.nc1603s39. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2009. PMID: 20013783 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of DNA/RNA and their analogs via phosphoramidite and H-phosphonate chemistries.Molecules. 2013 Nov 18;18(11):14268-84. doi: 10.3390/molecules181114268. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24252996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of gene silencing effect and membrane permeability by Peptide-conjugated 27-nucleotide small interfering RNA.Molecules. 2012 Sep 14;17(9):11089-102. doi: 10.3390/molecules170911089. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22983148 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Nucleotides for Chemical and Enzymatic Synthesis of Therapeutic RNA.Curr Med Chem. 2023;30(11):1320-1347. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666221014111403. Curr Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36239720
-
Chemical modification patterns compatible with high potency dicer-substrate small interfering RNAs.Oligonucleotides. 2008 Jun;18(2):187-200. doi: 10.1089/oli.2008.0123. Oligonucleotides. 2008. PMID: 18637735 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of MDR1 expression with altritol-modified siRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(4):1064-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl1126. Epub 2007 Jan 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17264131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denli A.M., Hannon G.J. RNAi: an ever-growing puzzle. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003;28:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Novina C.D., Sharp P.A. The RNAi revolution. Nature. 2004;430:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Meister G., Tuschl T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature. 2004;431:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G., Zamore P.D. RNAi: nature abhors a double-strand. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002;12:225–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

