Early apoptosis of blood monocytes in the septic host: is it a mechanism of protection in the event of septic shock?
- PMID: 16696867
- PMCID: PMC1550931
- DOI: 10.1186/cc4921
Early apoptosis of blood monocytes in the septic host: is it a mechanism of protection in the event of septic shock?
Abstract
Introduction: Based on the central role of the triggering of monocytes for the initiation of the septic cascade, it was investigated whether apoptosis of blood monocytes in septic patients is connected to their final outcome.
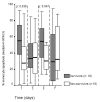
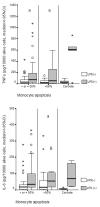
Methods: Blood monocytes were isolated from 90 patients with septic syndrome due to ventilator-associated pneumonia on days 1, 3, 5 and 7 from the initiation of symptoms. Apoptosis was defined after incubation with annexin-V-fluorescein isothiocyanate and propidium iodine and reading by a flow cytometer. The function of first-day monocytes was evaluated from the concentrations of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) and IL-6 in supernatants of cell cultures after triggering with endotoxins. TNFalpha, IL-6 and IL-8 were estimated in serum by an enzyme immunoassay.
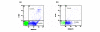
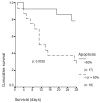
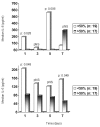
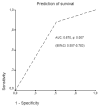
Results: Mortality rates of patients with apoptosis < or =50% compared with patients with apoptosis >50% were 49.12% and 15.15%, respectively (P < 0.0001). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a 28-day survival benefit in patients with septic shock and monocyte apoptosis >50% compared with those patients with apoptosis < or =50% (P = 0.0032). Production of IL-6 by monocytes on the first day by patients with apoptosis < or =50% was similar compared with monocytes isolated from healthy controls. Serum concentrations of TNFalpha were higher in patients with monocyte apoptosis < or =50% and septic shock compared with patients with apoptosis >50% on day 7; similar findings occurred for serum IL-6 on days 1 and 7 and for serum IL-8 on days 1 and 5.
Conclusion: Early apoptosis of monocytes upon presentation of clinical signs of sepsis is connected to a favourable outcome. These findings are of particular importance for the patient with septic shock, where they might constitute a mechanism of pathogenesis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Death of the septic monocyte: is more better?Crit Care. 2006;10(3):146. doi: 10.1186/cc4950. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Crit Care. 2006. PMID: 16762041 Free PMC article. Review.
Similar articles
-
Does soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 play any role in the pathogenesis of septic shock?Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Oct;142(1):62-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02887.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16178857 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of programmed death-1 on T cells and programmed death ligand-1 on monocytes in septic shock patients.Crit Care. 2011;15(1):R70. doi: 10.1186/cc10059. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21349174 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Circulating IL-10-Producing Cells in Septic Shock Patients: A Proof of Concept Study.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 4;11:615009. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.615009. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33613540 Free PMC article.
-
Angiopoietin-2 is increased in septic shock: evidence for the existence of a circulating factor stimulating its release from human monocytes.Immunol Lett. 2009 Jun 30;125(1):65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.06.006. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Immunol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19539650
-
Serum of patients with septic shock stimulates the expression of Trem-1 on U937 monocytes.Inflamm Res. 2009 Mar;58(3):127-32. doi: 10.1007/s00011-008-7039-4. Inflamm Res. 2009. PMID: 19109693
Cited by
-
Sepsis induced immunosuppression: Implications for secondary infections and complications.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2013 May;17(3):162-9. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.117054. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 24082613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIM22-Mediated Apoptosis is Associated with Bak Oligomerization in Monocytes.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 12;7:39961. doi: 10.1038/srep39961. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28079123 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio on survival in septic patients: an observational cohort study.Arch Med Sci. 2020 Jan 29;20(3):790-797. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.92692. eCollection 2024. Arch Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 39050157 Free PMC article.
-
The P2X7 Receptor Contributes to the Development of the Exacerbated Inflammatory Response Associated with Sepsis.J Innate Immun. 2015;7(4):417-27. doi: 10.1159/000371388. Epub 2015 Feb 13. J Innate Immun. 2015. PMID: 25675986 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of clarithromycin in inflammatory markers of patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia and sepsis caused by Gram-negative bacteria: results from a randomized clinical study.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jul;56(7):3819-25. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05798-11. Epub 2012 May 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22564837 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Adrie C, Bachelet M, Vayssier-Taussat M, Russo-Marie F, Bouchaert I, Adib-Conquy M, Cavaillon JM, Pinsky MR, Dhainaut JF, Polla BS. Mitochondrial membrane potential and apoptosis peripheral blood monocytes in severe human sepsis. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2001;164:389–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

