The RNA polymerase I transcription machinery
- PMID: 16626300
- PMCID: PMC3858827
- DOI: 10.1042/bss0730203
The RNA polymerase I transcription machinery
Abstract
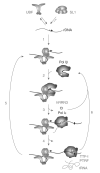
The rRNAs constitute the catalytic and structural components of the ribosome, the protein synthesis machinery of cells. The level of rRNA synthesis, mediated by Pol I (RNA polymerase I), therefore has a major impact on the life and destiny of a cell. In order to elucidate how cells achieve the stringent control of Pol I transcription, matching the supply of rRNA to demand under different cellular growth conditions, it is essential to understand the components and mechanics of the Pol I transcription machinery. In this review, we discuss: (i) the molecular composition and functions of the Pol I enzyme complex and the two main Pol I transcription factors, SL1 (selectivity factor 1) and UBF (upstream binding factor); (ii) the interplay between these factors during pre-initiation complex formation at the rDNA promoter in mammalian cells; and (iii) the cellular control of the Pol I transcription machinery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA polymerase I remains intact without subunit exchange through multiple rounds of transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 19;101(42):15112-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406746101. Epub 2004 Oct 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15477604 Free PMC article.
-
TBP-TAF complex SL1 directs RNA polymerase I pre-initiation complex formation and stabilizes upstream binding factor at the rDNA promoter.J Biol Chem. 2005 Aug 19;280(33):29551-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501595200. Epub 2005 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15970593 Free PMC article.
-
CK2-mediated stimulation of Pol I transcription by stabilization of UBF-SL1 interaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(17):4752-66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl581. Epub 2006 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16971462 Free PMC article.
-
Features of yeast RNA polymerase I with special consideration of the lobe binding subunits.Biol Chem. 2023 Oct 13;404(11-12):979-1002. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2023-0184. Print 2023 Oct 26. Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37823775 Review.
-
RNA-polymerase-I-directed rDNA transcription, life and works.Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 Feb;30(2):87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.12.008. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15691654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Polymerase I Is Uniquely Vulnerable to the Small-Molecule Inhibitor BMH-21.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;14(22):5544. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225544. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428638 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput assay for directly monitoring nucleolar rRNA biogenesis.Open Biol. 2022 Jan;12(1):210305. doi: 10.1098/rsob.210305. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Open Biol. 2022. PMID: 35078352 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature-dependent regulation of rDNA condensation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cell Cycle. 2017 Jun 3;16(11):1118-1127. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1317409. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28426272 Free PMC article.
-
The Mammalian and Yeast A49 and A34 Heterodimers: Homologous but Not the Same.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 22;12(5):620. doi: 10.3390/genes12050620. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome activity influences UV-mediated subnuclear localization changes of NPM.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059096. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grummt I. Genes Dev. 2003;17:1691–1702. - PubMed
-
- Moss T, Stefanovsky VY. Cell. 2002;109:545–548. - PubMed
-
- Reeder RH. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1999;62:293–327. - PubMed
-
- Hannan KM, Hannan RD, Rothblum LI. Front. Biosci. 1998;3:d376–d398. - PubMed
-
- Comai L. Adv. Protein Chem. 2004;67:123–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
