Characterization of COMMD protein-protein interactions in NF-kappaB signalling
- PMID: 16573520
- PMCID: PMC1525016
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051664
Characterization of COMMD protein-protein interactions in NF-kappaB signalling
Abstract
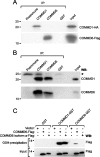
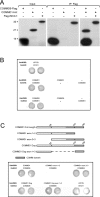
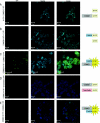
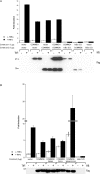
COMMD [copper metabolism gene MURR1 (mouse U2af1-rs1 region 1) domain] proteins constitute a recently identified family of NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB)-inhibiting proteins, characterized by the presence of the COMM domain. In the present paper, we report detailed investigation of the role of this protein family, and specifically the role of the COMM domain, in NF-kappaB signalling through characterization of protein-protein interactions involving COMMD proteins. The small ubiquitously expressed COMMD6 consists primarily of the COMM domain. Therefore COMMD1 and COMMD6 were analysed further as prototype members of the COMMD protein family. Using specific antisera, interaction between endogenous COMMD1 and COMMD6 is described. This interaction was verified by independent techniques, appeared to be direct and could be detected throughout the whole cell, including the nucleus. Both proteins inhibit TNF (tumour necrosis factor)-induced NF-kappaB activation in a non-synergistic manner. Mutation of the amino acid residues Trp24 and Pro41 in the COMM domain of COMMD6 completely abolished the inhibitory effect of COMMD6 on TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation, but this was not accompanied by loss of interaction with COMMD1, COMMD6 or the NF-kappaB subunit RelA. In contrast with COMMD1, COMMD6 does not bind to IkappaBalpha (inhibitory kappaBalpha), indicating that both proteins inhibit NF-kappaB in an overlapping, but not completely similar, manner. Taken together, these data support the significance of COMMD protein-protein interactions and provide new mechanistic insight into the function of this protein family in NF-kappaB signalling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
COMMD1 expression is controlled by critical residues that determine XIAP binding.Biochem J. 2009 Jan 15;417(2):601-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080854. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 18795889 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning NF-κB activity: a touch of COMMD proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2315-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.09.014. Epub 2013 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24080195 Review.
-
COMMD proteins, a novel family of structural and functional homologs of MURR1.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 10;280(23):22222-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501928200. Epub 2005 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15799966
-
Characterization and copper binding properties of human COMMD1 (MURR1).Biochemistry. 2007 Mar 20;46(11):3116-28. doi: 10.1021/bi0620656. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17309234
-
ABINs: A20 binding inhibitors of NF-kappa B and apoptosis signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 15;78(2):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19464428 Review.
Cited by
-
CCDC22 deficiency in humans blunts activation of proinflammatory NF-κB signaling.J Clin Invest. 2013 May;123(5):2244-56. doi: 10.1172/JCI66466. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23563313 Free PMC article.
-
Systems-wide Studies Uncover Commander, a Multiprotein Complex Essential to Human Development.Cell Syst. 2017 May 24;4(5):483-494. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2017.04.006. Cell Syst. 2017. PMID: 28544880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics analysis of the oncogenic value of copper Metabolism-Related protein COMMD2 in human cancers.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(10):11941-11959. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5320. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36205192 Free PMC article.
-
COMMD1 expression is controlled by critical residues that determine XIAP binding.Biochem J. 2009 Jan 15;417(2):601-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080854. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 18795889 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the COMMD4-H2B protein complex in lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2023 Dec;129(12):2014-2024. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02476-8. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37914802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burstein E., Hoberg J. E., Wilkinson A. S., Rumble J. M., Csomos R. A., Komarck C. M., Maine G. N., Wilkinson J. C., Mayo M. W., Duckett C. S. COMMD proteins, a novel family of structural and functional homologs of MURR1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:22222–22232. - PubMed
-
- van de Sluis B., Kole S., van Wolferen M., Holmes N. G., Pearson P. L., Rothuizen J., van Oost B. A., Wijmenga C. Refined genetic and comparative physical mapping of the canine copper toxicosis locus. Mamm. Genome. 2000;11:455–460. - PubMed
-
- van de Sluis B., Rothuizen J., Pearson P. L., van Oost B. A., Wijmenga C. Identification of a new copper metabolism gene by positional cloning in a purebred dog population. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002;11:165–173. - PubMed
-
- Klomp A. E., van de Sluis B., Klomp L. W., Wijmenga C. The ubiquitously expressed MURR1 protein is absent in canine copper toxicosis. J. Hepatol. 2003;39:703–709. - PubMed
-
- de Bie P., van De Sluis B., Klomp L., Wijmenga C. The many faces of the copper metabolism protein MURR1/COMMD1. J. Hered. 2005;96:803–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

