X-chromosome-wide profiling of MSL-1 distribution and dosage compensation in Drosophila
- PMID: 16547175
- PMCID: PMC1472288
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.377506
X-chromosome-wide profiling of MSL-1 distribution and dosage compensation in Drosophila
Abstract
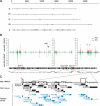
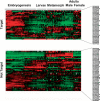
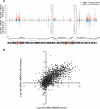
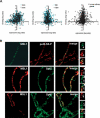
In Drosophila, dosage compensation is achieved by a twofold up-regulation of the male X-linked genes and requires the association of the male-specific lethal complex (MSL) on the X chromosome. How the MSL complex is targeted to X-linked genes and whether its recruitment at a local level is necessary and sufficient to ensure dosage compensation remain poorly understood. Here we report the MSL-1-binding profile along the male X chromosome in embryos and male salivary glands isolated from third instar larvae using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) coupled with DNA microarray (ChIP-chip). This analysis has revealed that majority of the MSL-1 targets are primarily expressed during early embryogenesis and many target genes possess DNA replication element factor (DREF)-binding sites in their promoters. In addition, we show that MSL-1 distribution remains stable across development and that binding of MSL-1 on X-chromosomal genes does not correlate with transcription in male salivary glands. These results show that transcription per se on the X chromosome cannot be the sole signal for MSL-1 recruitment. Furthermore, genome-wide analysis of the dosage-compensated status of X-linked genes in male and female shows that most of the X chromosome remains compensated without direct MSL-1 binding near the gene. Our results, therefore, provide a comprehensive overview of MSL-1 binding and dosage-compensated status of X-linked genes and suggest a more global effect of MSL complex on X-chromosome regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MSL complex associates with clusters of actively transcribed genes along the Drosophila male X chromosome.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:385-94. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.026. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381321
-
High-resolution ChIP-chip analysis reveals that the Drosophila MSL complex selectively identifies active genes on the male X chromosome.Genes Dev. 2006 Apr 1;20(7):848-57. doi: 10.1101/gad.1400206. Epub 2006 Mar 17. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16547173 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-wide gene-specific targeting of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex.Genes Dev. 2006 Apr 1;20(7):858-70. doi: 10.1101/gad.1399406. Epub 2006 Mar 17. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16547172 Free PMC article.
-
Path to equality strewn with roX.Dev Biol. 2004 May 1;269(1):18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.01.039. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15081354 Review.
-
The MSL complex: X chromosome and beyond.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010 Apr;20(2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.01.007. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010. PMID: 20167472 Review.
Cited by
-
Painting of fourth and chromosome-wide regulation of the 4th chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster.EMBO J. 2007 May 2;26(9):2307-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601604. Epub 2007 Feb 22. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17318176 Free PMC article.
-
Global patterns of sequence evolution in Drosophila.BMC Genomics. 2007 Nov 9;8:408. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-408. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17996078 Free PMC article.
-
A new strategy for isolating genes controlling dosage compensation in Drosophila using a simple epigenetic mosaic eye phenotype.BMC Biol. 2010 Jun 10;8:80. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-80. BMC Biol. 2010. PMID: 20537125 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting of the Y chromosome influences dosage compensation in roX1 roX2 Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2009 Nov;183(3):811-20. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.107219. Epub 2009 Aug 24. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19704014 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila MSL complex globally acetylates H4K16 on the male X chromosome for dosage compensation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Aug;16(8):825-32. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1644. Epub 2009 Aug 2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19648925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal B.D., Calvi B.R. Chromatin regulates origin activity in Drosophila follicle cells. Nature. 2004;430:372–376. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A., Becker P.B. Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyl transferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell. 2000;5:367–375. - PubMed
-
- Arbeitman M.N., Furlong E.E., Imam F., Johnson E., Null B.H., Baker B.S., Krasnow M.A., Scott M.P., Davis R.W., White K.P. Gene expression during the life cycle of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2002;297:2270–2275. - PubMed
-
- Baker B.S., Gorman M., Marin I. Dosage compensation in Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1994;28:491–521. - PubMed
-
- Belyakin S.N., Christophides G.K., Alekseyenko A.A., Kriventseva E.V., Belyaeva E.S., Nanayev R.A., Makunin I.V., Kafatos F.C., Zhimulev I.F. Genomic analysis of Drosophila chromosome underreplication reveals a link between replication control and transcriptional territories. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005;102:8269–8274. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
