Endocrine functions of bile acids
- PMID: 16541101
- PMCID: PMC1440314
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601049
Endocrine functions of bile acids
Abstract
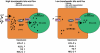
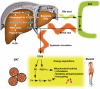
Bile acids (BAs), a group of structurally diverse molecules that are primarily synthesized in the liver from cholesterol, are the chief components of bile. Besides their well-established roles in dietary lipid absorption and cholesterol homeostasis, it has recently emerged that BAs are also signaling molecules, with systemic endocrine functions. BAs activate mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, are ligands for the G-protein-coupled receptor TGR5, and activate nuclear hormone receptors such as farnesoid X receptor alpha. Through activation of these diverse signaling pathways, BAs can regulate their own enterohepatic circulation, but also triglyceride, cholesterol, energy, and glucose homeostasis. Thus, BA-controlled signaling pathways are promising novel drug targets to treat common metabolic diseases, such as obesity, type II diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bile acids as regulators of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism.Dig Dis. 2010;28(1):220-4. doi: 10.1159/000282091. Epub 2010 May 7. Dig Dis. 2010. PMID: 20460915 Review.
-
Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation.Nature. 2006 Jan 26;439(7075):484-9. doi: 10.1038/nature04330. Epub 2006 Jan 8. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16400329
-
Bile acids and insulin resistance: implications for treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.J Dig Dis. 2009 May;10(2):85-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2009.00369.x. J Dig Dis. 2009. PMID: 19426389 Review.
-
Bile acids and signal transduction: role in glucose homeostasis.Cell Signal. 2008 Dec;20(12):2180-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.06.014. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18634871 Review.
-
The role of the enterohepatic circulation of bile salts and nuclear hormone receptors in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis: Bile salts as ligands for nuclear hormone receptors.Can J Gastroenterol. 2003 Apr;17(4):265-71. doi: 10.1155/2003/190784. Can J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12704471 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of transmembrane bile acid receptor TGR5 stimulates insulin secretion in pancreatic β cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Oct 26;427(3):600-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.104. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 23022524 Free PMC article.
-
The alpha-glucosidase inhibitor miglitol increases hepatic CYP7A1 activity in association with altered short-chain fatty acid production in the gut of obese diabetic mice.Metabol Open. 2020 Jan 11;5:100024. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2020.100024. eCollection 2020 Mar. Metabol Open. 2020. PMID: 32812937 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Roles of the Gut Microbiota in Pancreatic Carcinogenesis and Therapeutics.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Apr 6;12:872019. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.872019. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35463649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A top-down systems biology view of microbiome-mammalian metabolic interactions in a mouse model.Mol Syst Biol. 2007;3:112. doi: 10.1038/msb4100153. Epub 2007 May 22. Mol Syst Biol. 2007. PMID: 17515922 Free PMC article.
-
Global miRNA profiling reveals key molecules that contribute to different chronic lymphocytic leukemia incidences in Asian and Western populations.Haematologica. 2024 Feb 1;109(2):479-492. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283181. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 37646669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelin B, Einarsson K, Hellstrom K, Leijd B (1978) Effects of cholestyramine and chenodeoxycholic acid on the metabolism of endogenous triglyceride in hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res 19: 1017–1024 - PubMed
-
- Brendel C, Schoonjans K, Botrugno OA, Treuter E, Auwerx J (2002) The small heterodimer partner interacts with the liver X receptor alpha and represses its transcriptional activity. Mol Endocrinol 16: 2065–2076 - PubMed
-
- Chiang JY (2002) Bile acid regulation of gene expression: roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr Rev 23: 443–463 - PubMed
-
- Claudel T, Staels B, Kuipers F (2005) The farnesoid X receptor. A molecular link between bile acid and lipid and glucose metabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25: 2020–2030 - PubMed
-
- Cohen DE (2003) Pathogenesis of gallstones. In Hepatology: A Textbook of Liver Disease, Zakim D, Boyer TD (eds) pp 1713–1743. Philadelphia: Saunders
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

