Key stages in mammary gland development: the cues that regulate ductal branching morphogenesis
- PMID: 16524451
- PMCID: PMC1413974
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1368
Key stages in mammary gland development: the cues that regulate ductal branching morphogenesis
Abstract
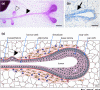
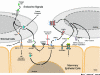
Part of how the mammary gland fulfills its function of producing and delivering adequate amounts of milk is by forming an extensive tree-like network of branched ducts from a rudimentary epithelial bud. This process, termed branching morphogenesis, begins in fetal development, pauses after birth, resumes in response to estrogens at puberty, and is refined in response to cyclic ovarian stimulation once the margins of the mammary fat pad are met. Thus it is driven by systemic hormonal stimuli that elicit local paracrine interactions between the developing epithelial ducts and their adjacent embryonic mesenchyme or postnatal stroma. This local cellular cross-talk, in turn, orchestrates the tissue remodeling that ultimately produces a mature ductal tree. Although the precise mechanisms are still unclear, our understanding of branching in the mammary gland and elsewhere is rapidly improving. Moreover, many of these mechanisms are hijacked, bypassed, or corrupted during the development and progression of cancer. Thus a clearer understanding of the underlying endocrine and paracrine pathways that regulate mammary branching may shed light on how they contribute to cancer and how their ill effects might be overcome or entirely avoided.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hormonal and local control of mammary branching morphogenesis.Differentiation. 2006 Sep;74(7):365-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2006.00105.x. Differentiation. 2006. PMID: 16916375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphogenesis of mammary gland development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004;554:219-28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4242-8_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004. PMID: 15384579 Review.
-
Molecular regulators of pubertal mammary gland development.Ann Med. 2011 May;43(3):212-34. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2011.554425. Epub 2011 Mar 20. Ann Med. 2011. PMID: 21417804 Review.
-
Activation and function of the epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB-2 during mammary gland morphogenesis.Cell Growth Differ. 1998 Sep;9(9):777-85. Cell Growth Differ. 1998. PMID: 9751121
-
Requirement of macrophages and eosinophils and their cytokines/chemokines for mammary gland development.Breast Cancer Res. 2002;4(4):155-64. doi: 10.1186/bcr441. Epub 2002 Jun 25. Breast Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12100741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Screening of Trehalose Synbiotics and Their Effects on Early-Lactating Females and Offspring Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;13(10):1223. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101223. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456476 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of gene expression in the development of early hyperplastic precursors of breast cancer.Am J Pathol. 2007 Jul;171(1):252-62. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.061010. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17591970 Free PMC article.
-
Illuminating the center: mechanisms regulating lumen formation and maintenance in mammary morphogenesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006 Oct;11(3-4):205-11. doi: 10.1007/s10911-006-9030-4. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 17115263 Review.
-
Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 11;10(1):4626. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12522-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31604923 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms regulating epithelial morphogenesis and cancer invasion.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;22(5):640-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.08.019. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20832275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

