Csk mediates G-protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptor-induced inhibition of membrane-bound guanylyl cyclase activity
- PMID: 16519534
- PMCID: PMC2519153
- DOI: 10.1021/bi052513u
Csk mediates G-protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptor-induced inhibition of membrane-bound guanylyl cyclase activity
Abstract
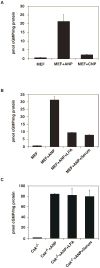
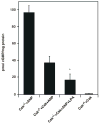
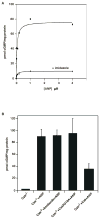
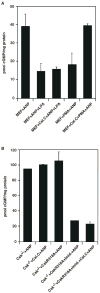
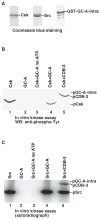
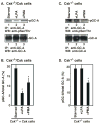
Natriuretic peptides (NPs) are involved in many physiological processes, including the regulation of vascular tone, sodium excretion, pressure-volume homeostasis, inflammatory responses, and cellular growth. The two main receptors of NP, membrane-bound guanylyl cyclases A and B (GC-A and GC-B), mediate the effects of NPs via the generation of cGMP. NP-stimulated generation of cGMP can be modulated by intracellular processes, whose exact nature remains to be elucidated. Thus, serum and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), by unknown pathways, have been shown to inhibit the NP-induced generation of cGMP. Here we report that the nonreceptor-tyrosine-kinase Csk is an essential component of the intracellular modulation of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)-stimulated activation of GC-A. The genetic deletion of Csk (Csk(-)(/)(-)) in mouse embryonic fibroblasts blocked the inhibitory effect of both serum and LPA on the ANP-stimulated generation of cGMP. Moreover, using a chemical rescue approach, we also demonstrate that the catalytic activity of Csk is required for its modulatory function. Our data demonstrate that Csk is involved in the control of cGMP levels and that membrane-bound guanylyl cyclases can be critically modulated by other receptor-initiated intracellular signaling pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Homologous and lysophosphatidic acid-induced desensitization of the atrial natriuretic peptide receptor, guanylyl cyclase-A, in MA-10 leydig cells.Endocrinology. 2006 Jun;147(6):2974-85. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0092. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16527839
-
Lysophosphatidic acid inhibits C-type natriuretic peptide activation of guanylyl cyclase-B.Endocrinology. 2003 Jan;144(1):240-6. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220702. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12488350
-
Different effects of soluble and particulate guanylyl cyclases on expression of inflammatory cytokines in rat peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Immunobiology. 2011 Mar;216(3):423-30. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2010.06.006. Epub 2010 Jul 24. Immunobiology. 2011. PMID: 20656372
-
The guanylyl cyclase receptor family.New Biol. 1990 Jun;2(6):499-504. New Biol. 1990. PMID: 1982420 Review.
-
Molecular physiology of natriuretic peptide signalling.Basic Res Cardiol. 2004 Mar;99(2):76-82. doi: 10.1007/s00395-004-0460-0. Epub 2004 Jan 23. Basic Res Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 14963665 Review.
Cited by
-
The chemical biology of protein phosphorylation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:797-825. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.070907.103047. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19489734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of targets of c-Src tyrosine kinase by chemical complementation and phosphoproteomics.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Aug;11(8):355-69. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.015750. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22499769 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Lysophosphatidic Acid in Cancer: The Issues in Moving from Bench to Bedside.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 10;11(10):1523. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101523. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31658655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brought to life: targeted activation of enzyme function with small molecules.J Chem Biol. 2009 Mar;2(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s12154-008-0012-4. Epub 2008 Sep 20. J Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19568788 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Guanylyl Cyclase (GC)-A and Other Membrane GC Receptors.Endocr Rev. 2024 Sep 12;45(5):755-771. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnae015. Endocr Rev. 2024. PMID: 38713083 Review.
References
-
- Silberbach M, Roberts CT., Jr Natriuretic peptide signalling: molecular and cellular pathways to growth regulation. Cell Signal. 2001;13:221–31. - PubMed
-
- Wedel B, Garbers D. The guanylyl cyclase family at Y2K. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:215–33. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn M. Structure, regulation, and function of mammalian membrane guanylyl cyclase receptors, with a focus on guanylyl cyclase-A. Circ Res. 2003;93:700–9. - PubMed
-
- Chrisman TD, Schulz S, Potter LR, Garbers DL. Seminal plasma factors that cause large elevations in cellular cyclic GMP are C-type natriuretic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:3698–703. - PubMed
-
- Atlas SA, Kleinert HD, Camargo MJ, Januszewicz A, Sealey JE, Laragh JH, Schilling JW, Lewicki JA, Johnson LK, Maack T. Purification, sequencing and synthesis of natriuretic and vasoactive rat atrial peptide. Nature. 1984;309:717–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

