Estrogen receptors and human disease
- PMID: 16511588
- PMCID: PMC2373424
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI27987
Estrogen receptors and human disease
Abstract
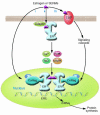
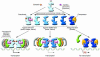
Estrogens influence many physiological processes in mammals, including but not limited to reproduction, cardiovascular health, bone integrity, cognition, and behavior. Given this widespread role for estrogen in human physiology, it is not surprising that estrogen is also implicated in the development or progression of numerous diseases, which include but are not limited to various types of cancer (breast, ovarian, colorectal, prostate, endometrial), osteoporosis, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance, lupus erythematosus, endometriosis, and obesity. In many of these diseases, estrogen mediates its effects through the estrogen receptor (ER), which serves as the basis for many therapeutic interventions. This Review will describe diseases in which estrogen, through the ER, plays a role in the development or severity of disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estrogen receptors and endocrine diseases: lessons from estrogen receptor knockout mice.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;1(6):613-9. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4892(01)00105-9. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11757817 Review.
-
Lessons from the dissection of the activation functions (AF-1 and AF-2) of the estrogen receptor alpha in vivo.Steroids. 2013 Jun;78(6):576-82. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2012.11.011. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Steroids. 2013. PMID: 23200732 Review.
-
The Case for an Estrogen-iron Axis in Health and Disease.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2020 Apr;128(4):270-277. doi: 10.1055/a-0885-1677. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 30978727
-
Estrogen(s) and analogs as a non-immunogenic endogenous ligand in targeted drug/DNA delivery.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(19):2095-109. doi: 10.2174/092986707781368432. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17691950 Review.
-
Estrogen receptors and human disease: an update.Arch Toxicol. 2012 Oct;86(10):1491-504. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0868-5. Epub 2012 May 31. Arch Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22648069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment-related risk factors for arm lymphedema among long-term breast cancer survivors.J Cancer Surviv. 2015 Sep;9(3):422-30. doi: 10.1007/s11764-014-0416-9. Epub 2015 Apr 26. J Cancer Surviv. 2015. PMID: 25913877
-
The role of maintenance proteins in the preservation of epithelial cell identity during mammary gland remodeling and breast cancer initiation.Chin J Cancer. 2014 Feb;33(2):51-67. doi: 10.5732/cjc.013.10040. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Chin J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23845141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A semi-supervised method for drug-target interaction prediction with consistency in networks.PLoS One. 2013 May 7;8(5):e62975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062975. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667553 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptors and their implications in colorectal carcinogenesis.Front Oncol. 2015 Feb 2;5:19. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00019. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25699240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposures to synthetic estrogens at different times during the life, and their effect on breast cancer risk.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2013 Mar;18(1):25-42. doi: 10.1007/s10911-013-9274-8. Epub 2013 Feb 8. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23392570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mueller SO, Korach KS. Estrogen receptors and endocrine diseases: lessons from estrogen receptor knockout mice. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2001;1:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Couse JF, Korach KS. Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr. Rev. 1999;20:358–417. - PubMed
-
- Herynk MH, Fuqua SA. Estrogen receptor mutations in human disease. Endocr. Rev. 2004;25:869–898. - PubMed
-
- Fabian CJ, Kimler BF. Selective estrogen-receptor modulators for primary prevention of breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23:1644–1655. - PubMed
-
- Shang Y, Brown M. Molecular determinants for the tissue specificity of SERMs. Science. 2002;295:2465–2468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

