Autophagy-mediated clearance of huntingtin aggregates triggered by the insulin-signaling pathway
- PMID: 16505167
- PMCID: PMC2063704
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200510065
Autophagy-mediated clearance of huntingtin aggregates triggered by the insulin-signaling pathway
Abstract
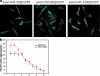
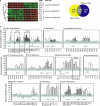
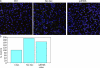
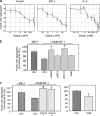
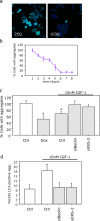
Conditional mouse models of polyglutamine diseases, such as Huntington's disease (HD), have revealed that cells can clear accumulated pathogenic proteins if the continuous production of the mutant transgene is halted. Invariably, the clearance of the protein leads to regression of the disease symptoms in mice. In light of these findings, it is critical to determine the pathway responsible for alleviating this protein accumulation to define targets to fight these diseases. In a functional genetic screen of HD, we found that activation of insulin receptor substrate-2, which mediates the signaling cascades of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1, leads to a macroautophagy-mediated clearance of the accumulated proteins. The macroautophagy is triggered despite activation of Akt, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and S6 kinase, but still requires proteins previously implicated in macroautophagy, such as Beclin1 and hVps34. These findings indicate that the accumulation of mutant protein can lead to mTOR-independent macroautophagy and that lysosome-mediated degradation of accumulated protein differs from degradation under conditions of starvation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The regulation of N-terminal Huntingtin (Htt552) accumulation by Beclin1.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Jun;33(6):743-51. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.14. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22543707 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin and mTOR-independent autophagy inducers ameliorate toxicity of polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin and related proteinopathies.Cell Death Differ. 2009 Jan;16(1):46-56. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.110. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Cell Death Differ. 2009. PMID: 18636076 Review.
-
Raised intracellular glucose concentrations reduce aggregation and cell death caused by mutant huntingtin exon 1 by decreasing mTOR phosphorylation and inducing autophagy.Hum Mol Genet. 2003 May 1;12(9):985-94. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg109. Hum Mol Genet. 2003. PMID: 12700167
-
Differential ERK activation during autophagy induced by europium hydroxide nanorods and trehalose: Maximum clearance of huntingtin aggregates through combined treatment.Biomaterials. 2015 Dec;73:160-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26409001
-
Insulin htts on autophagy.Autophagy. 2006 Jul-Sep;2(3):250-3. doi: 10.4161/auto.2788. Epub 2006 Jul 10. Autophagy. 2006. PMID: 16874093 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of an autophagy inducer J3 to lower mutant huntingtin and alleviate Huntington's disease-related phenotype.Cell Biosci. 2022 Oct 8;12(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00906-3. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36209136 Free PMC article.
-
Function and characteristics of PINK1 in mitochondria.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:601587. doi: 10.1155/2013/601587. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 23533695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological activation of Sirt1 ameliorates polyglutamine-induced toxicity through the regulation of autophagy.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 10;8(6):e64953. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064953. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762270 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-1 receptor antagonism inhibits autophagy.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Nov 15;22(22):4528-44. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt300. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23804751 Free PMC article.
-
Macroautophagy in CNS health and disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022 Jul;23(7):411-427. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00588-3. Epub 2022 May 3. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35505254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrejewski, N., E.L. Punnonen, G. Guhde, Y. Tanaka, R. Lullmann-Rauch, D. Hartmann, K. von Figura, and P. Saftig. 1999. Normal lysosomal morphology and function in LAMP-1-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 274:12692–12701. - PubMed
-
- Arrasate, M., S. Mitra, E.S. Schweitzer, M.R. Segal, and S. Finkbeiner. 2004. Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature. 431:805–810. - PubMed
-
- Backer, J.M. 2000. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases and the regulation of vesicular trafficking. Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun. 3:193–204. - PubMed
-
- Bence, N.F., R.M. Sampat, and R.R. Kopito. 2001. Impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by protein aggregation. Science. 292:1552–1555. - PubMed
-
- Blommaart, E.F., U. Krause, J.P. Schellens, H. Vreeling-Sindelarova, and A.J. Meijer. 1997. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors wortmannin and LY294002 inhibit autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes. Eur. J. Biochem. 243:240–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

