Role of transforming growth factor-beta in hematologic malignancies
- PMID: 16484590
- PMCID: PMC1895802
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-10-4169
Role of transforming growth factor-beta in hematologic malignancies
Abstract
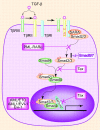
The transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling pathway is an essential regulator of cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, migration, and cell survival. During hematopoiesis, the TGF-beta signaling pathway is a potent negative regulator of proliferation while stimulating differentiation and apoptosis when appropriate. In hematologic malignancies, including leukemias, myeloproliferative disorders, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma, resistance to these homeostatic effects of TGF-beta develops. Mechanisms for this resistance include mutation or deletion of members of the TGF-beta signaling pathway and disruption of the pathway by oncoproteins. These alterations define a tumor suppressor role for the TGF-beta pathway in human hematologic malignancies. On the other hand, elevated levels of TGF-beta can promote myelofibrosis and the pathogenesis of some hematologic malignancies through their effects on the stroma and immune system. Advances in the TGF-beta signaling field should enable targeting of the TGF-beta signaling pathway for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of transforming growth factor Beta in human cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2005 Mar 20;23(9):2078-93. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.047. J Clin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15774796 Review.
-
MUC1 in hematological malignancies.Leuk Lymphoma. 2016 Nov;57(11):2489-98. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2016.1195500. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016. PMID: 27347699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in normal and malignant hematopoiesis.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2007 Jul;27(7):543-52. doi: 10.1089/jir.2007.0009. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2007. PMID: 17651015 Review.
-
LRG1 modulates invasion and migration of glioma cell lines through TGF-β signaling pathway.Acta Histochem. 2015 Jul;117(6):551-8. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Acta Histochem. 2015. PMID: 26049667
-
Targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor in hematologic malignancies.Eur J Haematol. 2012 Nov;89(5):373-84. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12009. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Eur J Haematol. 2012. PMID: 22928557 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting TGF-β signaling in cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Jul;17(7):743-60. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.782287. Epub 2013 May 7. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23651053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SPAG6 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis via TGF-β/Smad signal pathway in adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Int J Hematol. 2024 Feb;119(2):119-129. doi: 10.1007/s12185-023-03684-x. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Int J Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38147275
-
The Impact of NLRP3 Activation on Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 31;22(21):11845. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111845. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive characterization of TGFB1 across hematological malignancies.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 4;13(1):19107. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46552-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37925591 Free PMC article.
-
Zfyve16 regulates the proliferation of B-lymphoid cells.Front Med. 2018 Oct;12(5):559-565. doi: 10.1007/s11684-017-0562-3. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Front Med. 2018. PMID: 29247407
References
-
- Elliott RL, Blobe GC. Role of transforming growth factor Beta in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23: 2078-2093. - PubMed
-
- Attisano L, Wrana JL. Signal transduction by the TGF-beta superfamily. Science. 2002;296: 1646-1647. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113: 685-700. - PubMed
-
- Derynck R, Zhang YE. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature. 2003;425: 577-584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

