Binding specificity of Toll-like receptor cytoplasmic domains
- PMID: 16482509
- PMCID: PMC2762736
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200535158
Binding specificity of Toll-like receptor cytoplasmic domains
Abstract
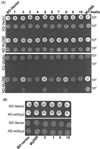
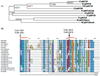
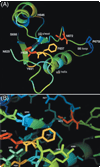
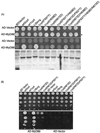
MyD88 participates in signal transduction by binding to the cytoplasmic Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domains of activated Toll-like receptors (TLR). Yeast two-hybrid experiments reveal that the TIR domains of human TLR differ in their ability to associate with MyD88: The TIR of TLR2 binds to MyD88 but the TIR of the closely related TLR1, 6, or 10 do not. Using chimeric TIR domains, we define the critical region responsible for differential MyD88 binding, and use a computational analysis of the critical region to reveal the amino acids that differ between MyD88 binders and non-binders. Remarkably, a single missense mutation created in TLR1 (N672D) confers on it the ability to bind MyD88, without affecting its association with other proteins. Mutations identified as critical for MyD88 binding also affect signaling of TLR pairs in mammalian cells. To investigate the difference between MyD88 binders and non-binders, we identify novel interacting proteins for each cytoplasmic domain of TLR1, 2, 6, and 10. For example, heat shock protein (HSP)60 binds to TLR1 but not to TLR2, and HSP60 and MyD88 appear to bind the same region of the TIR domain. In summary, interactions between the TLR, MyD88, and novel associated proteins have been characterized.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis identifies residues crucial for homodimerization of myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) and for its function in immune cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 18;288(42):30210-30222. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.490946. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24019529 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the binding mode of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain proteins during TLR2 signaling.Mol Immunol. 2012 Oct;52(3-4):108-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22673208
-
Microcrystal electron diffraction structure of Toll-like receptor 2 TIR-domain-nucleated MyD88 TIR-domain higher-order assembly.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024 Sep 1;80(Pt 9):699-712. doi: 10.1107/S2059798324008210. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 39268708 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, function and regulation of the Toll/IL-1 receptor adaptor proteins.Immunol Cell Biol. 2007 Aug-Sep;85(6):411-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100095. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Immunol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17667936 Review.
-
Summary and comparison of the signaling mechanisms of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor family.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Nov 11;1592(3):265-80. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(02)00320-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12421671 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of MyD88-dependent TLR1/2 signaling by misfolded α-synuclein, a protein linked to neurodegenerative disorders.Sci Signal. 2015 May 12;8(376):ra45. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005965. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 25969543 Free PMC article.
-
A promiscuous lipid-binding protein diversifies the subcellular sites of toll-like receptor signal transduction.Cell. 2014 Feb 13;156(4):705-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.019. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24529375 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional evidence for the role of the TLR2 DD loop in TLR1/TLR2 heterodimerization and signaling.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 6;281(40):30132-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602057200. Epub 2006 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16893894 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the multiple interactions of the MyD88 TIR domain in TLR4 signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 23;106(25):10260-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812956106. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19506249 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of interaction sites for dimerization and adapter recruitment in Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain of Toll-like receptor 4.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 3;287(6):4088-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.282350. Epub 2011 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22139835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takeda K, Akira S. TLR signaling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 2004;16:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Nishiya T, DeFranco AL. Ligand-regulated chimeric receptor approach reveals distinctive subcellular localization and signaling properties of the Toll-like receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:19008–19017. - PubMed
-
- Hajjar AM, O'Mahony DS, Ozinsky A, Underhill DM, Aderem A, Klebanoff SJ, Wilson CB. Cutting Edge: Functional interactions between Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR1 or TLR6 in response to phenol-soluble modulin. J. Immunol. 2001;166:15–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

