Alcohol potently modulates climbing fiber-->Purkinje neuron synapses: role of metabotropic glutamate receptors
- PMID: 16481422
- PMCID: PMC6674936
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4430-05.2006
Alcohol potently modulates climbing fiber-->Purkinje neuron synapses: role of metabotropic glutamate receptors
Abstract
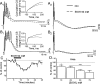
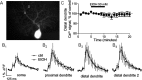
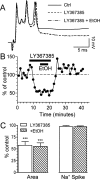
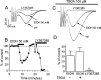
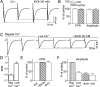
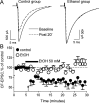
Consumption of alcoholic beverages produces alterations in motor coordination and equilibrium that are responsible for millions of accidental deaths. Studies indicate that ethanol produces these alterations by affecting the cerebellum, a brain region involved in the control of motor systems. Purkinje neurons of the cerebellar cortex have been shown to be particularly important targets of ethanol. However, its mechanism of action at these neurons is poorly understood. We hypothesized that ethanol could modulate Purkinje neuron function by altering the excitatory input provided by the climbing fiber from the inferior olive, which evokes a powerful all-or-none response denoted as the complex spike. To test this hypothesis, we performed whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiological and Ca2+ imaging experiments in acute slices from rat cerebella. We found that ethanol potently inhibits the late phase of the complex spike and that this effect is the result of inhibition of type-1 metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent responses at the postsynaptic level. Moreover, ethanol inhibited climbing fiber long-term depression, a form of synaptic plasticity that also depends on activation of these metabotropic receptors. Our findings identify the climbing fiber-->Purkinje neuron synapse as an important target of ethanol in the cerebellar cortex and indicate that ethanol significantly affects cerebellar circuits even at concentrations as low as 10 mm (legal blood alcohol level in the United States is below 0.08 g/dl = 17 mm).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alcohol impairs long-term depression at the cerebellar parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapse.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Dec;100(6):3167-74. doi: 10.1152/jn.90384.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 15. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18922952 Free PMC article.
-
Third trimester-equivalent ethanol exposure does not alter complex spikes and climbing fiber long-term depression in cerebellar Purkinje neurons from juvenile rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 May;38(5):1293-300. doi: 10.1111/acer.12362. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 24689500 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated currents at the climbing fiber to Purkinje cell synapse.J Chem Inf Model. 2005 Nov-Dec;45(6):1536-8. doi: 10.1021/ci050161s. J Chem Inf Model. 2005. PMID: 16309250
-
Pharmacology of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mediated current at the climbing fiber to Purkinje cell synapse.Prog Brain Res. 2005;148:299-306. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(04)48023-6. Prog Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15661198 Review.
-
Glutamate-receptor-like molecule GluRδ2 involved in synapse formation at parallel fiber-Purkinje neuron synapses.Cerebellum. 2012 Mar;11(1):71-7. doi: 10.1007/s12311-010-0170-0. Cerebellum. 2012. PMID: 20387025 Review.
Cited by
-
LTD-like molecular pathways in developmental synaptic pruning.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Sep 27;19(10):1299-310. doi: 10.1038/nn.4389. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27669991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Ethanol Consumption Impairs the Tactile-Evoked Long-Term Depression at Cerebellar Molecular Layer Interneuron-Purkinje Cell Synapses in vivo in Mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jan 14;12:521. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00521. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30692916 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol decreases Purkinje neuron excitability by increasing GABA release in rat cerebellar slices.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Dec;327(3):910-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.144865. Epub 2008 Aug 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18755936 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-Review: Effects of Ethanol on GABAA Receptor-Mediated Neurotransmission in the Cerebellar Cortex--Recent Advances.Cerebellum. 2015 Aug;14(4):438-46. doi: 10.1007/s12311-014-0639-3. Cerebellum. 2015. PMID: 25575727 Review.
-
Comparative assessments of the effects of alcohol exposure on fetal brain development using optical coherence tomography and ultrasound imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2013 Feb;18(2):20506. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.2.020506. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23386196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Autti-Ramo I, Autti T, Korkman M, Kettunen S, Salonen O, Valanne L (2002). MRI findings in children with school problems who had been exposed prenatally to alcohol. Dev Med Child Neurol 44:98–106. - PubMed
-
- Basile A, Hoffer B, Dunwiddie T (1983). Differential sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje neurons to ethanol in selectively outbred lines of mice: maintenance in vitro independent of synaptic transmission. Brain Res 264:69–78. - PubMed
-
- Brenowitz SD, Regehr WG (2005). Associative short-term synaptic plasticity mediated by endocannabinoids. Neuron 45:419–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
