Differential modulatory effects of annexin 1 on nitric oxide synthase induction by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages
- PMID: 16476053
- PMCID: PMC1782228
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02307.x
Differential modulatory effects of annexin 1 on nitric oxide synthase induction by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages
Abstract
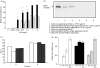
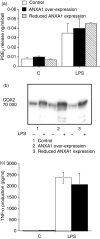
Annexin-1 (ANXA1) is a glucocorticoid-regulated protein that modulates the effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on macrophages. Exogenous administration of peptides derived from the N-terminus of ANXA1 reduces LPS-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, but the effects of altering the endogenous expression of this protein are unclear. We transfected RAW264.7 murine macrophage-like cell lines to over-express constitutively ANXA1 and investigated whether this protein modulates the induction of iNOS, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in response to LPS. In contrast to exogenous administration of N-terminal peptides, endogenous over-expression of ANXA1 results in up-regulation of LPS-induced iNOS protein expression and activity. However, levels of iNOS mRNA are unchanged. ANXA1 has no effect on COX-2 or TNF-alpha production in response to LPS. In experiments to investigate the mechanisms underlying these phenomena we observed that activation of signalling proteins classically associated with iNOS transcription was unaffected. Over-expression of ANXA1 constitutively activates extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK)-1 and ERK-2, components of a signalling pathway not previously recognized as regulating LPS-induced iNOS expression. Inhibition of ERK activity, by the inhibitor U0126, reduced LPS-induced iNOS expression in our cell lines. Over-expression of ANXA1 also modified LPS-induced phosphorylation of the ERK-regulated translational regulation factor eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Our data suggest that ANXA1 may modify iNOS levels by post-transcriptional mechanisms. Thus differential effects on iNOS expression in macrophages are seen when comparing acute administration of ANXA1 peptides versus the chronic endogenous over-expression of ANXA1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Janus kinase 3 inhibitor WHI-P154 in macrophages activated by bacterial endotoxin: differential effects on the expression of iNOS, COX-2 and TNF-alpha.Int Immunopharmacol. 2008 Jan;8(1):100-8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2007.10.016. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18068105
-
Inhibition of inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression by (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide in interferon-gamma- and bacterial lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Jan;316(1):121-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.093179. Epub 2005 Sep 15. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16166270
-
Effects of acute ethanol administration on LPS-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat alveolar macrophages.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Dec;29(12 Suppl):285S-93S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000191809.29775.41. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16385238
-
Annexin 1: more than an anti-phospholipase protein.Inflamm Res. 2004 Apr;53(4):125-32. doi: 10.1007/s00011-003-1235-z. Epub 2004 Mar 18. Inflamm Res. 2004. PMID: 15060718 Review.
-
Annexin A1 and the Resolution of Inflammation: Modulation of Neutrophil Recruitment, Apoptosis, and Clearance.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:8239258. doi: 10.1155/2016/8239258. Epub 2016 Jan 13. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 26885535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dexamethasone modulates Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in vivo independently of the glucocorticoid-inducible protein annexin-A1.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008 Dec;54(3):339-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00485.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 19049646 Free PMC article.
-
Pathobiological functions and clinical implications of annexin dysregulation in human cancers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 28;10:1009908. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1009908. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36247003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging enhances the production of reactive oxygen species and bactericidal activity in peritoneal macrophages by upregulating classical activation pathways.Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 15;50(45):9911-22. doi: 10.1021/bi2011866. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21981794 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Effects of ANXA1 in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: A Protection Mechanism?Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2015 Nov 26;21:241-6. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.895487. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2015. PMID: 26609771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raynal P, Pollard HB. Annexins. the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1197:63–93. - PubMed
-
- Flower RJ, Rothwell NJ. Lipocortin-1: cellular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994;15:71–6. - PubMed
-
- Diakonova M, Gerke V, Ernst J, Liautard JP, van der Vusse G, Griffiths G. Localization of five annexins in J774 macrophages and on isolated phagosomes. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:1199–213. - PubMed
-
- Traverso V, Morris JF, Flower RJ, Buckingham J. Lipocortin 1 (annexin 1) in patches associated with the membrane of a lung adenocarcinoma cell line and in the cell cytoplasm. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:1405–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

